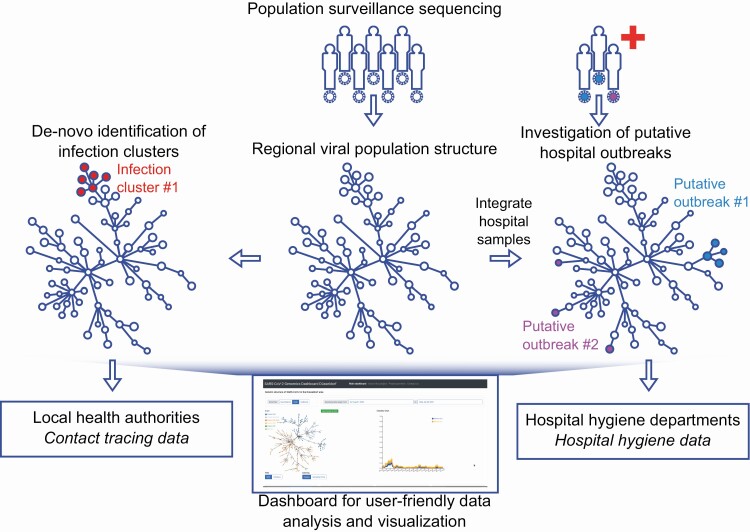
Figure 1.
Integrated genomic surveillance in the Düsseldorf area. Population surveillance sequencing enables the characterization of local SARS-CoV-2 population structure, facilitating the discrimination between clonal hospital outbreaks (here: putative outbreak 1) or simultaneously detected but unrelated SARS-CoV-2 hospital ward cases (here: putative outbreak 2). Viral population surveillance data can also enable the de novo identification of infection clusters in the population based on the genetic data. Added value of genomic surveillance is maximized when genetic data are integrated with complementary epidemiological data or approaches, such as contact tracing or hospital outbreak data. Utilization of viral genetic data by diverse stakeholders is facilitated by providing a user-friendly real-time web application (“dashboard”) for analysis and visualization of the generated viral genomes. Abbreviation: SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.