Fig. 5.
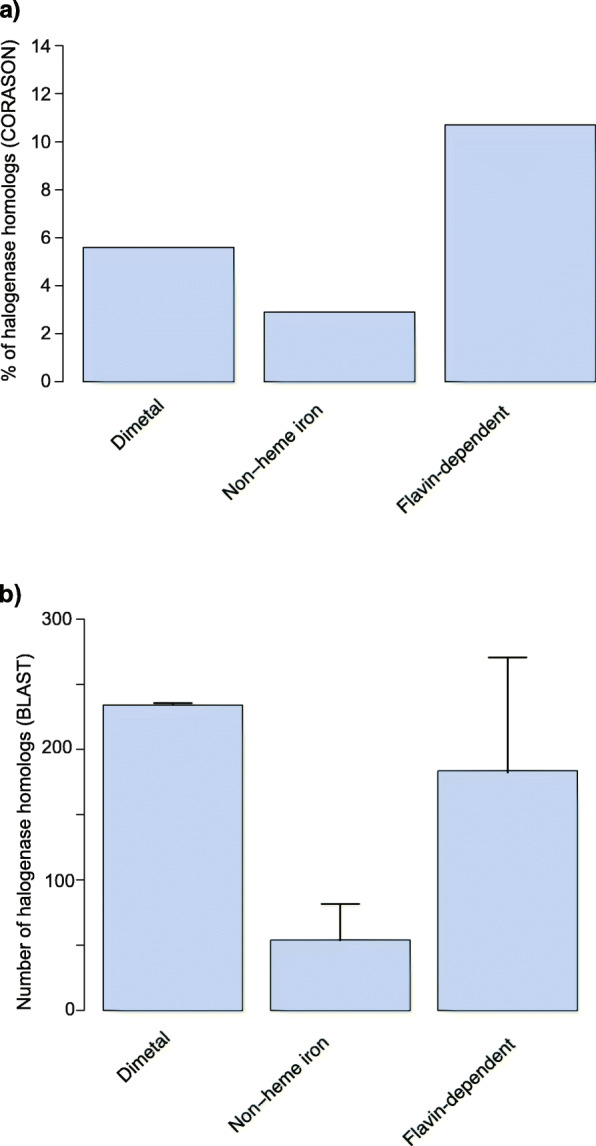
Prevalence of putative cyanobacterial halogenases. Frequency of halogenase homologs in Cyanobacteria from CORASON analysis (a) and NCBI BLASTp analysis (a). Dimetal-carboxylate halogenases: CylC - NCBI reference genomes, n = 2054 and LEGEcc genomes, n = 41 CylC-containing BGCs and 56 genomes; Flavin-dependent halogenases: PrnA - NCBI reference genomes, n = 2051 and LEGEcc genomes, n = 56 genomes; Bmp5- NCBI reference genomes, n = 2050 and LEGEcc genomes, n = 56 genomes; McnD: NCBI reference genomes, n = 2052 and LEGEcc genomes, n = 54 genomes; Nonheme iron/2OG-dependent halogenases: halogenase domain from CurA - NCBI reference genomes, n = 2052 and LEGEcc genomes, n = 56 genomes. B Average of the total number of homologs per dimetal-carboxylate halogenases (CylC, BrtJ, “Mic”, ColD, ColE, NocO, NocN), flavin-dependent halogenases (PrnA, Bmp5 and McnD) and nonheme iron/2OG-dependent halogenases (Barb1, HctB, WelO5, AmbO5 and the halogenase domain from CurA)
