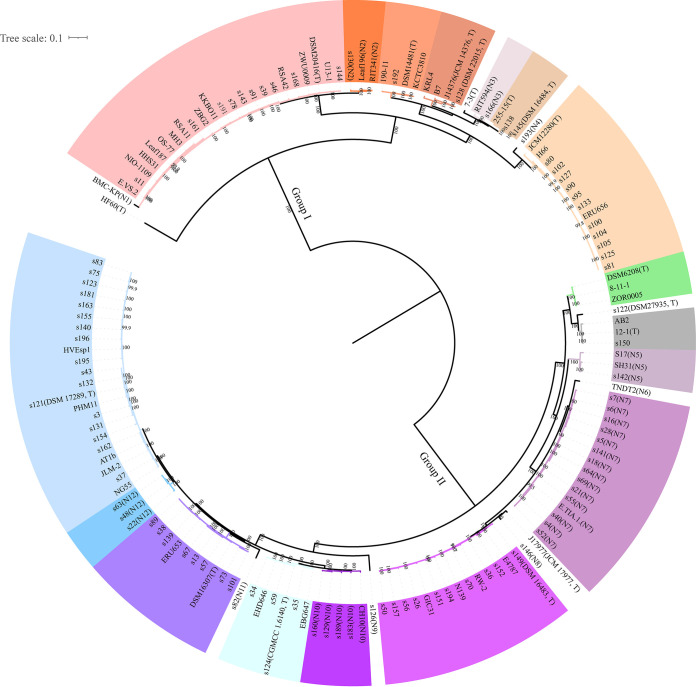
FIG 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of Exiguobacterium. The tree was built using IQ-TREE based on the concatenated amino acid sequence alignments of single-copy core genes. Bootstrap support values were calculated from 1,000 replicates. “T” represents the type strain for the following: NIO-1109 for E. enclense, HHS31 for E. indicum, DSM20416 for E. acetylicum, DSM14481 for E. undae, J14376 for E. soli, s128 for E. soli, 7-3 for E. sibiricum, 255-15 for E. sibiricum, s145 for E. artemiae, JCM12280 for E. oxidotolerans, DSM6208 for E. aurantiacum, s122 for “E. himgiriensis,” 12-1 for E. alkaliphilum, J17977 for E. aquaticum, s149 for E. mexicanum, s124 for E. aestuarii, DSM16307 for E. marinum, and s121 for E. profundum. N1 to N12 represent putative new species. Different colors represent different putative species, which were differentiated using the threshold ANI of 95%.