FIG. 7.
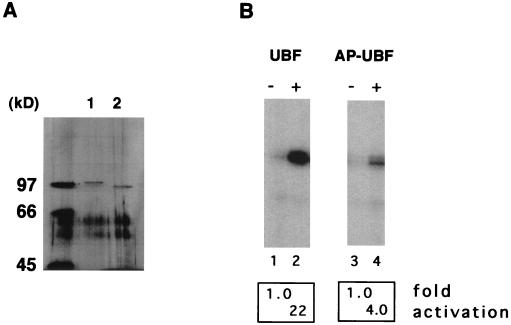
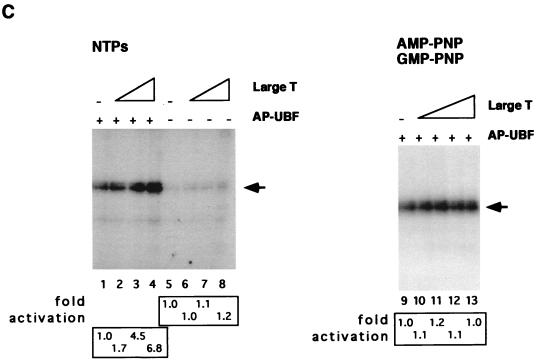
Large T antigen stimulates UBF-dependent transcription in the presence of AP-UBF. (A) UBF was expressed as a flag epitope-tagged protein by using recombinant baculovirus. Untreated UBF (lane 1) and AP-UBF (lane 2) were affinity purified by using anti-flag M2 beads. The concentration of each purified protein was determined by silver staining following SDS-PAGE. (B) In vitro transcription assays with untreated UBF (lane 2) and AP-UBF (lane 4). Transcription assays contained no UBF (lanes 1 and 3), approximately 0.25 ng of UBF (lane 2), or 0.25 ng of AP-UBF (lane 4). (C) Large T antigen stimulation of Pol I transcription in the absence of UBF (lanes 5 to 8) or in the presence of 0.25 ng of AP-UBF (lanes 1 to 4) as determined by in vitro reconstituted transcription assays. Each transcription reaction mixture contained either no large T antigen (lanes 1 and 5) or increasing amounts of purified large T antigen (50 to 250 ng; lanes 2 to 4 and 6 to 8). In lanes 9 to 13, nucleotide analogs AMP-PNP and GMP-PNP replaced ATP and GTP, respectively, in the transcription assay with 0.25 ng of AP-UBF. Each transcription reaction mixture contains either no large T antigen (lane 9) or increasing amounts of purified large T antigen (50 to 250 ng; lanes 10 to 13). The arrow indicates the position of the protected oligonucleotide fragment. (D) In vitro transcriptional activation by differentially treated UBF. Baculovirus expressed flag-tagged UBF immobilized on anti-flag M2 beads was either mock treated (lane 2), treated with alkaline phosphatase only (lane 3), or first treated with alkaline phosphatase and then incubated with purified large T antigen in the presence of either ATP (lanes 4 and 5) or AMP-PNP (lane 6). Following extensive washing, UBF proteins were then eluted from the affinity resin and dialyzed. An equal amount of protein, as determined by silver staining (data not shown), was tested for the ability to activate transcription in vitro. Transcription data were quantitated, and the fold activations are as indicated.