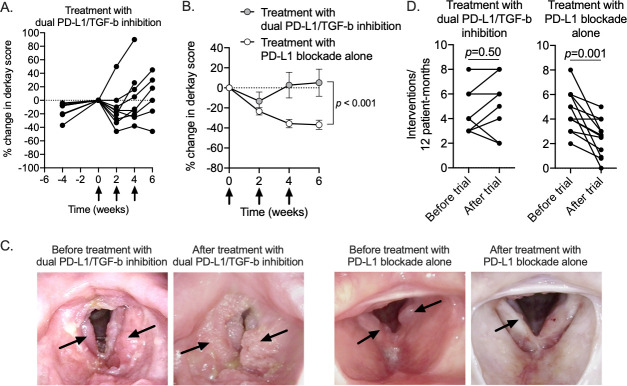
Figure 1.
Clinical responses following treatment with PD-L1/TGF-b inhibition or PD-L1 blockade alone in patients with recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. (A) Spider plot of change in laryngeal disease burden following treatment with dual PD-L1/TGF-b inhibition (n=9) as measured by anatomic Derkay score are shown. Negative time points on the x-axis indicate disease burden at the time of clinical trial screening. Treatment was initiated at time 0. Per cent change relative to disease burden at time 0. (B) Summary results demonstrating change in laryngeal disease burden following treatment with dual PD-L1/TGF-b inhibition (gray circles) or PD-L1 blockade alone (white circles) as previously reported. P value determined by comparing multiple means over multiple timepoints using the Holm-Sidak method. (C) Representative endoscopic still images from clinic laryngoscopy of patients treated with dual PD-L1/TGF-b inhibition or PD-L1 blockade alone. Black arrows indicate papillomatous disease. (D) Changes in the number of clinically indicated interventions per 12 patient months for patients treated with dual PD-L1/TGF-b inhibition or PD-L1 blockade alone are shown. P value determined by Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; TGF-b, transforming growth factor-beta.