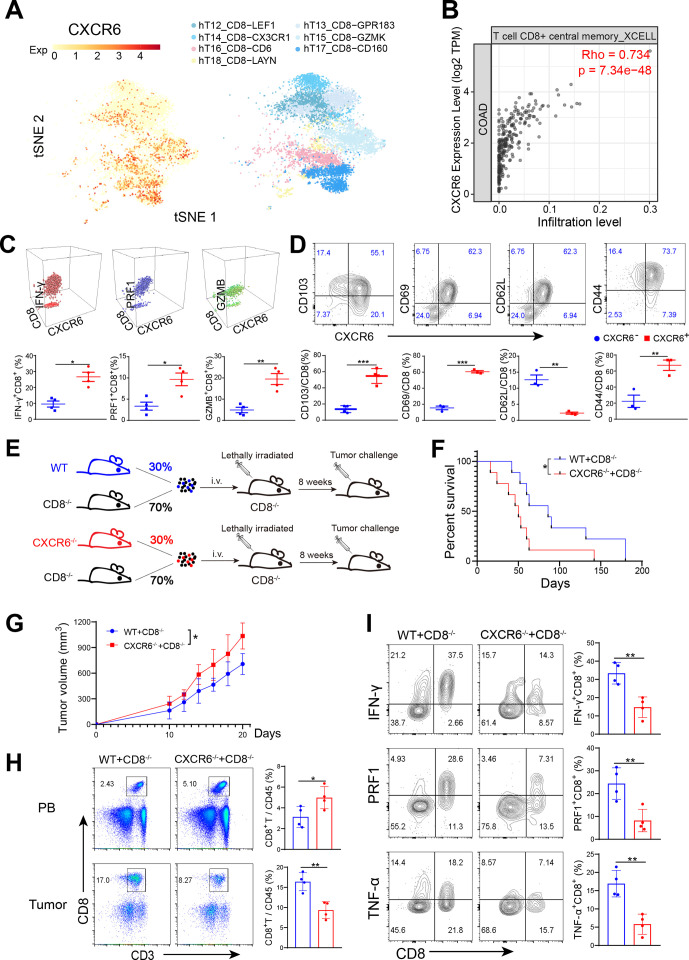
Figure 2.
CXCR6-deficient CD8+ T cells show weaker antitumor activity. (A) t-SNE plot showing CD8+ T cell clusters (right) and expression of CXCR6 (left) from human CRC. (B) Scatterplots showing correlation between CXCR6 expression and CD8+ T cell infiltration level in COAD in TCGA database determined by tumor immune estimation resource (timer, http://cistrome.dfci.harvard.edu/TIMER/) website. (C and D) Phenotypic characterization of CXCR6+CD8+ T and CXCR6−CD8+ T cells from MC38 tumors. (E) Set-up of bone marrow chimeric mice. Total bone marrow obtained from Cxcr6−/− or wild-type mice were mixed with that obtained from Cd8−/− mice and then transferred to lethally irradiated Cd8−/− recipients. Eight weeks later, challenged chimeras with MC38 tumor cells. (F and G). survival (F) and tumor growth (G) of tumor load chimeric mice (n=9–10 mice per group). (H) Quantification of CD8+ T cells from tumors. (I) Frequencies of cytokine-producing CD8+ T cells. *P<0.05 and **p<0.01. CXCR6, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 6.