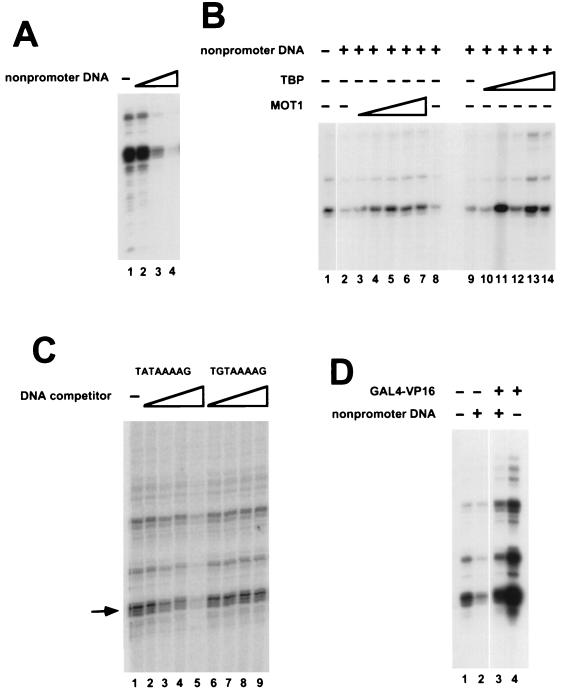
FIG. 6.
Repression of HIS4 basal transcription by nonpromoter DNA and effects of addition of TBP or GAL4-VP16. (A) Transcription reactions were performed with nuclear extract from mot1-1 cells. The reaction mixtures contained 0 μg (lane 1), 0.24 μg (lane 2), 1.2 μg (lane 3), or 2.4 μg (lane 4) of pKS II+ plasmid in addition to 0.25 μg of HIS4-containing plasmid template (see Materials and Methods). (B) Transcription reaction mixtures contained either 0 μg (lane 1) or 0.8 μg (lanes 2 to 14) of pKS II+. MOT1 purified from yeast was added to lanes 3 to 7 (0.5, 1.25, 2.5, 5, or 7.5 U, respectively); lane 8 contains a volume of mock-purified MOT1 equivalent to the volume of MOT1 added to lane 7. In addition to the TBP already present in the extract, recombinant yeast TBP was added to reaction mixtures in lanes 10 to 14 (1, 3, 10, 20, or 30 ng, respectively). The minus symbols in other lanes indicate that reaction mixtures contained TBP present in the nuclear extract but no additional recombinant TBP was added to the reaction. (C) HIS4 core promoter activity was assayed in the absence (lane 1) or presence of 50-mer oligonucleotide duplexes containing a wild-type TATA sequence (lanes 2 to 5) or a mutant TATA sequence, TGTAAAAG, which does not bind TBP (lanes 6 to 9). The reaction mixtures contained 3 ng (lanes 2 and 6), 10 ng (lanes 3 and 7), 30 ng (lanes 4 and 8), or 100 ng (lanes 5 and 9) of the indicated competitor oligonucleotides. (D) Transcription reaction mixtures contained pKS II+ (lanes 2 and 3) and/or GAL4-VP16 which was preincubated with DNA prior to the addition of mot1-1 nuclear extract. GAL4-VP16 activated transcription fivefold in the absence of pKS II+ and fourfold in the presence of pKS II+.