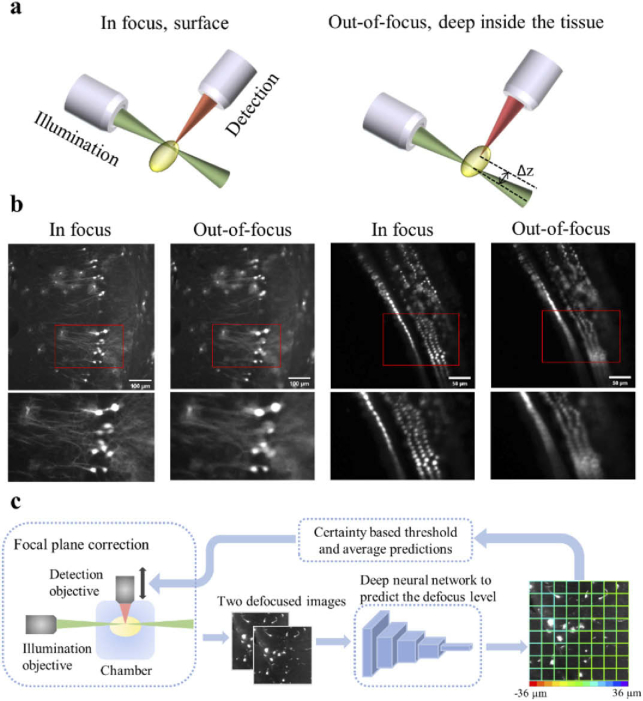
Fig. 1.
A schematic of the light-sheet excitation-detection module and the proposed deep neural network-based autofocus workflow. (a) An illustration of the geometry of light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM), and the drift in the relative position of the light-sheet and the focal plane of the detection objective (Δz), when imaging deep into the tissue. (b) Fluorescence images of in focus and out-of-focus neurons (left) and hair cells (right). The images were captured from a whole mouse brain and a pig cochlea that were tissue cleared for 3D volume imaging. The red boxes mark the locations of the zoom-in images at the bottom. The degradation in the quality of out-of-focus images can be observed. (c) Overview of the integration of the deep learning-based autofocus method with a custom-built LSFM. During image acquisition, two defocused images will be collected and sent to a classification network to estimate the defocus level. The color of the borders of each individual patch in the right image indicates the predicted defocus distance. In the color bar, the red and purple colors represent the extreme cases, in which the defocus distance is −36 µm and 36 µm respectively. The borders’ dominant color is green, which indicates that this image is in focus.