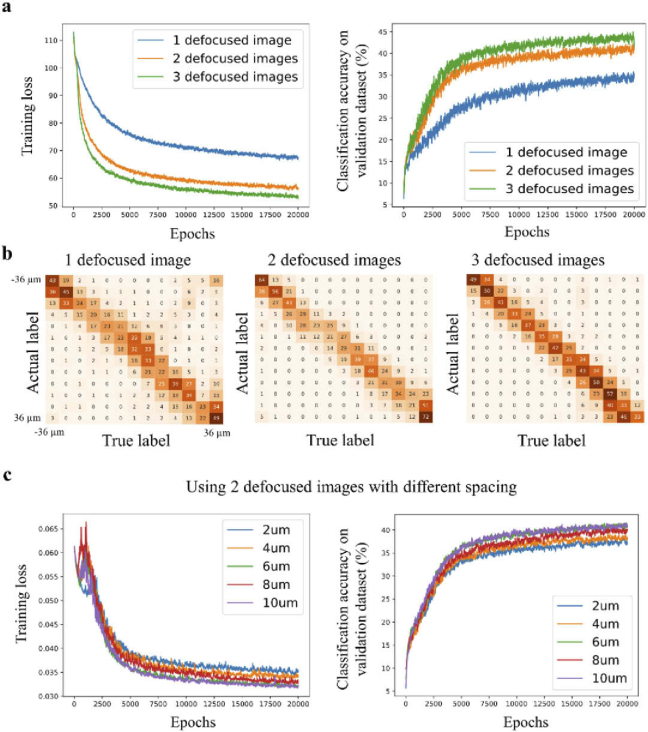
Fig. 3.
Training configurations that influence the classification accuracy. (a) The graphs show the training loss and classification accuracy as a function of the number of epochs. For comparison, the network is trained with one\two\three defocused images that are provided to the network as an input (N = 13, Δs = 6 μm). The graphs show that two (IΔz and ) and three (, , and ) defocus images yield higher classification accuracy than a single defocused image . (b) Confusion matrices for a different number of defocused images that are provided to the network as input. Training with only one defocused stack shows inferior performance. (c) Training loss and classification accuracy as a function of the number of epochs using 2 defocused images as an input, but with variable spacing between the images. The highest classification accuracy corresponds to values of 6 and 10 μm.