Figure 2.
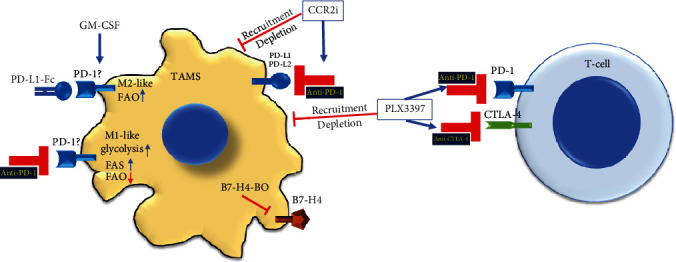
Examples of TAM combinatory targeting with immune checkpoint inhibitors. TAM depletion and recruitment inhibition to the tumor microenvironment, by CCR2 inhibitor or PLX3397, potentiate immune checkpoint inhibition by anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1/2, or anti-CTLA-4 and further stimulate T-cell functions. Similarly, inhibition of B7-H4 by specific morpholino antisense oligonucleotides (B7-H4-BO) contributes to T-cell stimulation, tumor regression, and tumor growth inhibition. In addition, under GM-CSF-induced macrophages, increased PD-1 expression, and manipulation either with PD-1 agonist (PD-L1-Fc) or with anti-PD-1 may favor the M2-like phenotype or M1-like phenotype, respectively, alongside metabolic reprogramming, which needed to be confirmed in TAMs. PD-1: programmed death protein-1; PD-L1: programmed death protein-ligand-1; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; FAO: fatty acid oxidation; FAS: fatty acid synthesis; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
