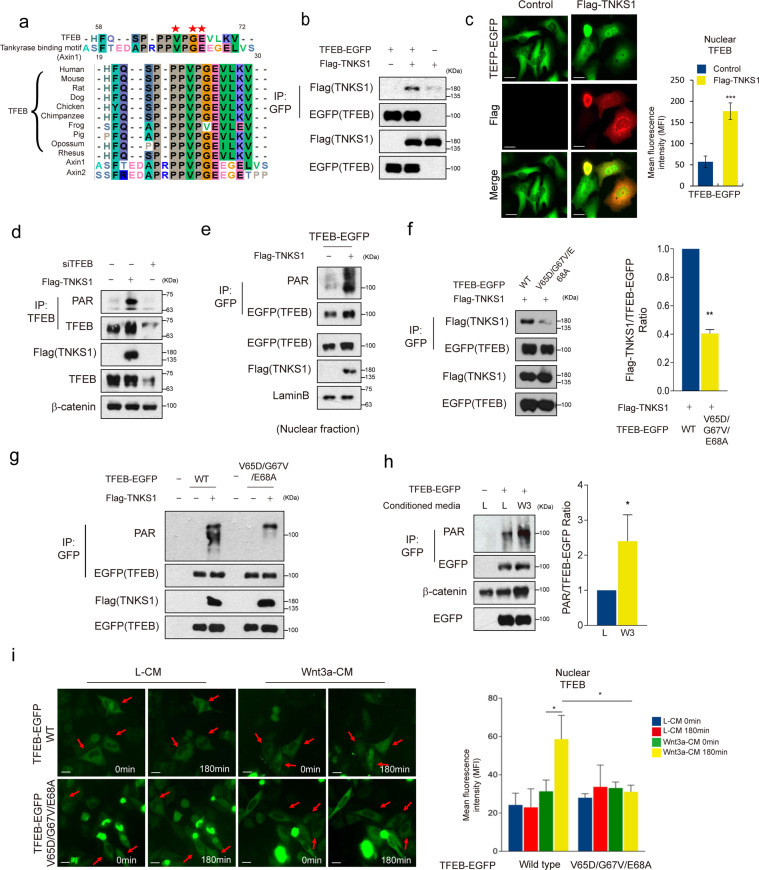
Fig. 3. Wnt signaling regulates TNKS1 mediated PARsylation of TFEB, followed by dissociation from destruction complex to nuclear localization.
a The TNKS1 binding motif of TFEB is evolutionarily conserved. Colored are the highly conserved sequences. b TFEB interacted with TNKS1. TFEB-EGFP and Flag-TNKS1 were co-transfected into HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. c Overexpression of TNKS1 induced nuclear localization of TFEB. TFEB-EGFP stable cells were transfected with the corresponding plasmid as indicated and were the subjected to IF analysis. Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of TFEB in the nuclear ROI region from 8 bit confocal images (maximum gray value, 256) was shown in the right panel. Scale bar, 20 μm. d Overexpression of TNKS1 induced PARsylation of TFEB. Flag-TNKS1 was transfected into HeLa cells. Cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing the poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase inhibitor, ADP-HPD (5 μM). Lysates were then immunoprecipitated with anti-TFEB antibody and immunoblotted with Poly(ADP-Ribose)Polymer antibody. e Nuclear TFEB was highly PARsylated by overexpression of TNKS1. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and nuclear lysates were used in immunoprecipitations. Nuclear lysates and immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. f Val-65, Gly-67 and Glu-68 of TFEB are required for interaction with TNKS1. Flag-TNKS1 with TFEB-EGFP or TFEB-EGFP mutant were transfected into HEK293T cells and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Quantification of the ratio of immunoprecipitated Flag-TNKS1/TFEB-EGFP of three independent immunoblots was shown in the right panel. g Mutant form of TFEB, which has a lower affinity for TNKS1 than the wild type TFEB, showed a reduced level of PARsylation under the TNKS1 overexpression condition. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. h Treatment with Wnt3a-CM increased PARsylation of TFEB. TFEB-EGFP expressing HEK293T cells were treated with Wnt3a-CM for 4 h. Cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing poly (ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase inhibitor, ADP-HPD (5 μM). Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and immunoblotted with PARsylation (PAR) specific antibody. Quantification of the ratio of immunoprecipitated PARsylated TFEB/TFEB-EGFP of three independent immunoblots was shown in the right panel. i Treatment with Wnt3a-CM induced nuclear localization of wild type TFEB, but not TNKS-binding deficient TFEB mutant. HeLa cells transfected with TFEB-EGFP or TFEB-EGFP-DVA plasmid were treated with L-CM or Wnt3a-CM. Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of TFEB in the nuclear ROI region from 8 bit confocal images (maximum gray value, 256) was shown in right panel. Scale bar, 20 μm.