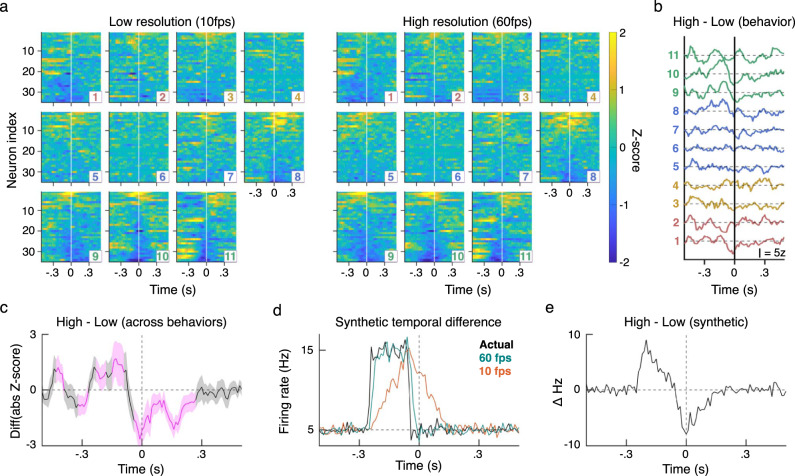
Fig. 3. Frameshifted high-temporal resolution improves identification of neural signatures at behavioral initiation.
a Z-scored neural activity aligned to the 11 B-SOiD identified behaviors using either low temporal resolution, non-frameshifted or high-resolution, and frameshifted alignment. Neurons and neuron order are the same for each pair of behavior panels. Detailed plots can be found in Supplementary Fig. 5. b Total signal magnitude difference (high - low resolution) for each of the behaviors (1 on bottom). Scale bar = 5 z-score difference. Colors as in Fig. 1c. c Mean and SEM of signal magnitude difference across all behaviors (magenta = p < 0.01, two-tailed t-test). Positive values indicate greater signal magnitude for high vs low temporal resolution. d Using simulated data, we measured the average firing rate with zero (Actual), high resolution (60 fps), or low-resolution (10 fps) temporal jitter introduced. 60 fps produced a considerably more accurate account of the ground truth model. e Incorporating features from our recording data, the model produces similar high-low resolution difference dynamics to (c), here in a spiking artificial neuron. Source data are provided as a Source Data file for (a).