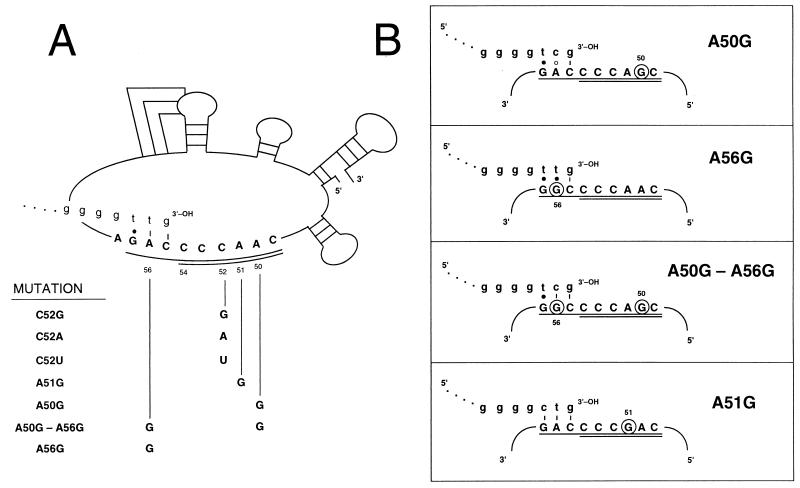
FIG. 1.
(A) P. tetraurelia telomerase RNA nucleotide substitutions. A schematic of the Paramecium telomerase RNA secondary structure and nucleotide positions is taken from reference 40. Alignment nucleotides (1) are underlined and templating nucleotides are double-underlined. The 3′ end of a de novo telomere is shown (lowercase letters) base paired with the alignment nucleotides prior to elongation by telomerase. The various mutations analyzed are identified by the wild-type telomerase RNA position followed by the altered nucleotide. (B) Base-pairing potential of telomeric repeats with mutated telomerase RNAs. Only the telomerase RNA alignment (underlined) and templating (doubly underlined) nucleotides are shown. Substituted nucleotides are circled, and the 3′ end of the predicted de novo telomere is shown in lowercase letters, base paired with the alignment region prior to elongation. Dashes represent Watson-Crick base pairs, solid circles represent rG · dT pairs, and open circles represent mismatched nucleotides.