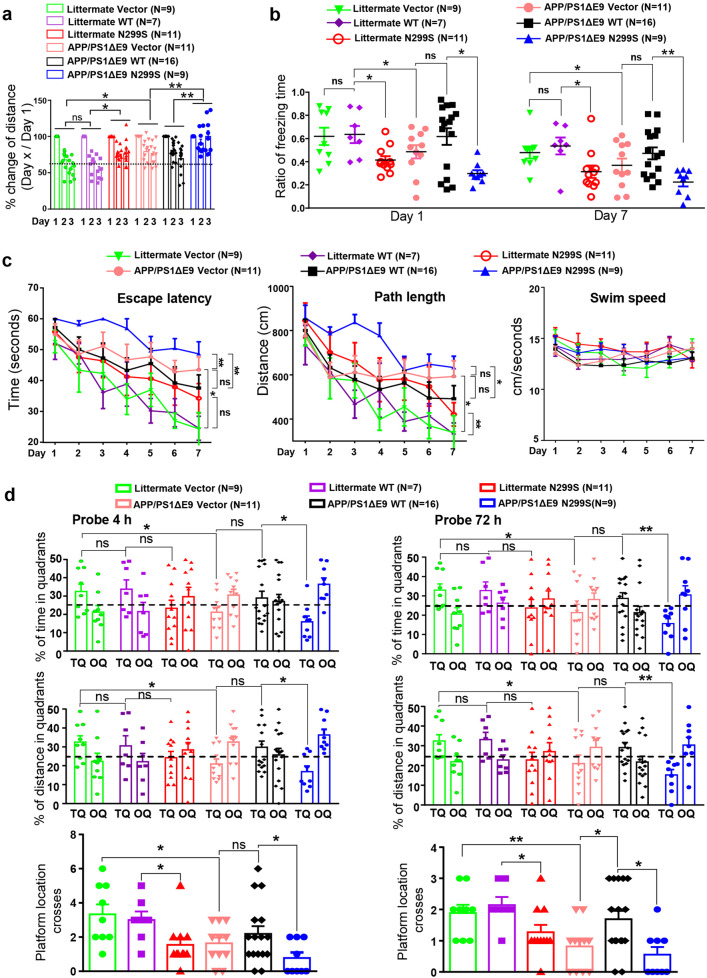
Fig. 3.
ACAA1 p.N299S aggravated memory impairments in APP/PS1ΔE9 mice. a Impaired habituation in the exploratory open field for APP/PS1 mice (8-month-old) and wild-type littermates with delivery of AAV-ACAA1 N299S versus AAV-ACAA1 WT or empty vector. The changes of distance traveled on days 2 and 3 were normalized to the distance traveled on day 1 of training. Data are mean ± SEM. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA. b ACAA1 p.N299S accelerated memory retrieval impairment of APP/PS1 and WT mice in fear conditioning tests. Shown data are the percentages of freezing time after 1 day (left) and 7 days (right) of electric shocks. Data are mean ± SEM. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with the Tukey’s post hoc test. c, d Morris water maze tests of APP/PS1ΔE9 mice or WT littermates with delivery of AAV empty vector or AAV-mediated expression of ACAA1 WT and ACAA1 N299S. The APP/PS1ΔE9 mice or WT littermates with AAV-Vector, AAV-ACAA1 WT, or AAV-ACAA1 N299S injection showed differences in escape latency, path length, and swim speed during learning session (c) and in probe trial performance at 4 h (short-term memory; left panel) and at 72 h (right panel) (d). TQ target quadrant (percentage of time and percentage of distance in the target quadrant), OQ opposite quadrant. Bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA with the Tukey’s post hoc test