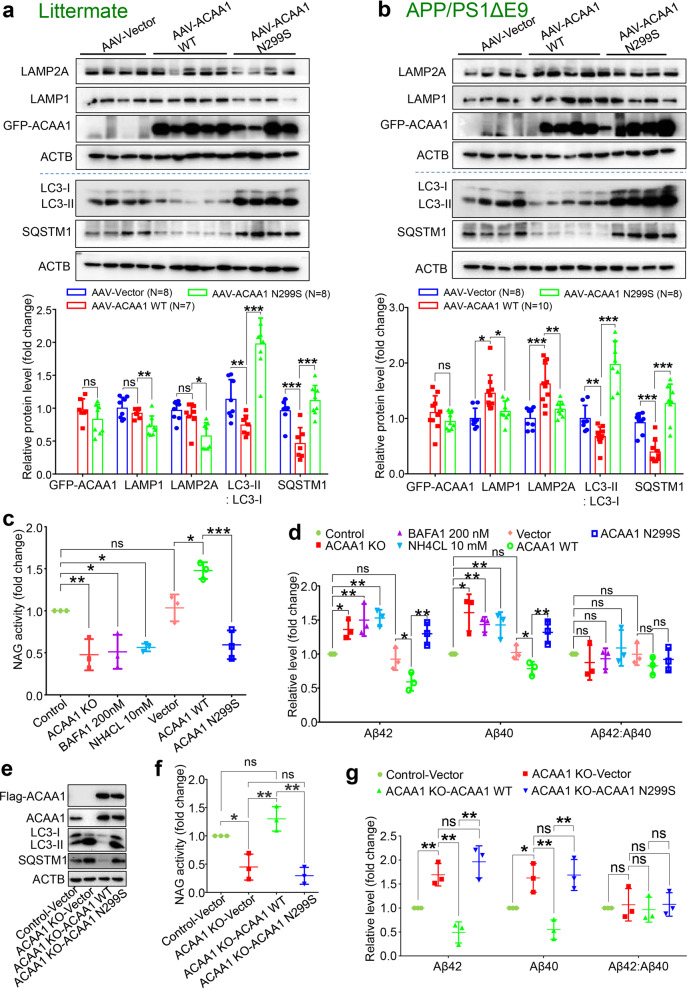
Fig. 6.
Effect of ACAA1 p.N299S on Aβ pathology was mediated by lysosomal dysfunction. a, b Western blot analysis of lysosomal proteins LAMP1 and LAMP2A and autophagy markers LC3-II:LC3-I ratio and SQSTM1 in the hippocampus tissues of WT littermates (a) and APP/PS1∆E9 (b) injected with AAV-ACAAA WT or AAV-ACAA1 N299S. Bars represent mean ± SD. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Student’s t test. (c) ACAA1 knockout (KO) or overexpression of ACAA1 p.N299S in U251-APP cells decreased NAG activity. Cells were treated with BAFA1 (200 nM), NH4CL (10 mM), or without treatment (Control) or were transfected with empty vector (Vector) and expression vector of ACAA1 WT, or ACAA1 p.N299S. d Levels of extracellular Aβ42, Aβ40, and Aβ42:Aβ40 ratio in the culture supernatants of U251-APP cells and U251-APP ACAA1 KO cells. e–g Overexpression of ACAA1 WT, but not ACAA1 p.N299S, in U251-APP ACAA1 KO cells had a rescuing effect on the altered protein levels of autophagy markers (e), lysosomal markers (f), and the levels of extracellular Aβ42 and Aβ40 in the culture supernatant (g). The U251-APP cells without ACAA1 knockout was used as a control, and cells were transfected with empty vector (Vector) and expression vector of ACAA1 WT or ACAA1 p.N299S. Data in e–g were based on three independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± SD. ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; Student’s t test