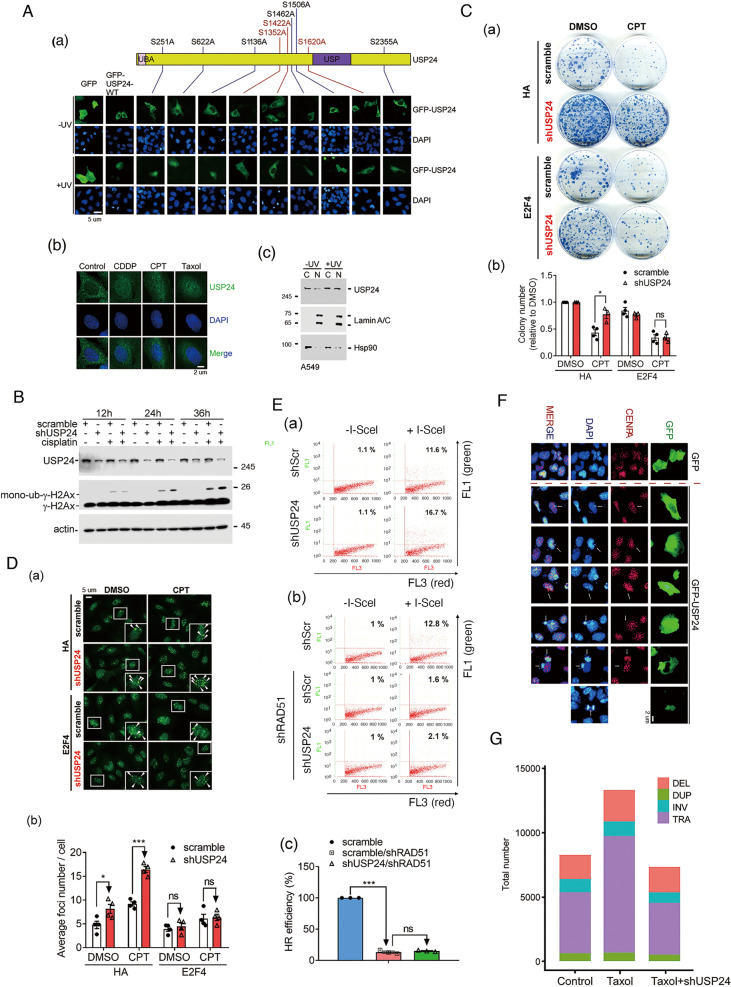
Fig. 5. USP24 enters the nucleus to induce genomic instability.
The localization of GFP, GFP-USP24 and various mutants of GFP-USP24 under normal or UV exposure conditions was studied by IF (A(a)). The level of USP24 in the cytoplasm and nuclei of A549 cells treated with CDDP, CPT, and Taxol (A(b)) with or without UV exposure (A(c)) was studied by IF and IB with the indicated antibodies. The levels of γ-H2AX and monoubiquitinated γ-H2AX in A549 cells with or without USP24 knockdown and cisplatin treatment were studied by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies (B). The viability of A549 cells treated with CPT, with or without USP24 knockdown and E2F4 overexpression was studied by colony-formation assay (C). The Rad51 foci was studied by anti-Rad51 antibodies in A549 cells with or without E2F4 overexpression and USP24 knockdown (D). HR-mediated DDR was studied by flow cytometry assay in A549 cells with or without knockdown of Rad51 and USP24 (E). The localization of GFP, GFP-USP24, CENPA, and DAPI was studied by IF with the indicated antibodies (F). The whole genomes of A549, T24, and USP24-knockdown T24 cells were sequenced by WGS and analyzed using Circos software to study the structure variants (SVs) (G). The results from three independent experiments were statistically analyzed using a t-test: *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005.