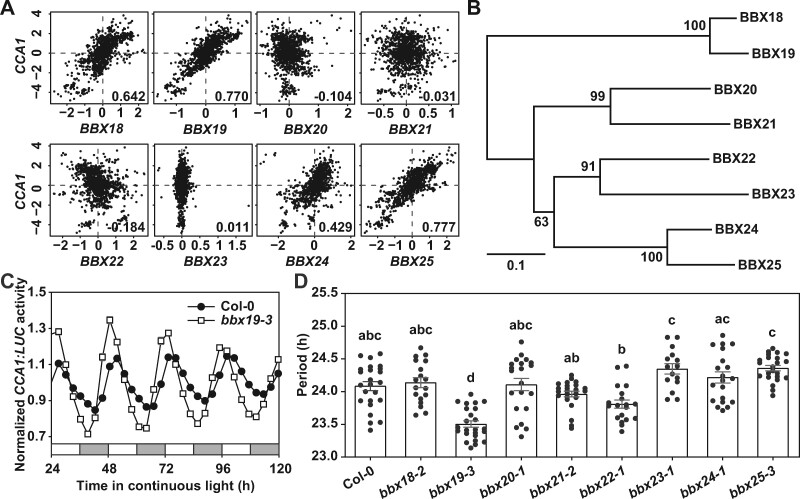
Figure 1.
Dysfunction of BBX19 leads to the accelerated circadian pace. A, Estimation of correlation between CCA1 and BBX subfamily IV genes in co-expression analysis using the multiple microarray- and RNAseq-based coexpression data sets in ATTED-II (http://atted.jp/top_draw.shtml#CoexViewer). The Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r-value) was listed in the lower right corner of each panel, which is used to represent the linear association between CCA1 and BBX subfamily genes. The r-value of 0 indicates that there is no association, while values of −1 or +1 indicates that there is a strongest linear correlation. B, The phylogenetic radiant tree of eight full-length orthologs of BBX subfamily IV in Arabidopsis. The evolutionary distance was inferred using the neighbor-joining method, and phylogenetic tree was constructed using the Jukes–Cantor genetic distance model in Geneious Tree Builder. C, D, Circadian rhythms of CCA1:LUC in the bbx18-bbx25 mutants were monitored under free-running conditions. Data showing mean ± se for three independent experiments. At least 15 individual seedlings were used for each analysis. Open bars indicate subjective day, and gray bars indicate subjective night (C). Dots indicate individual samples and bars mean period ± se (D). Multiple groups were analyzed with one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test, P < 0.05