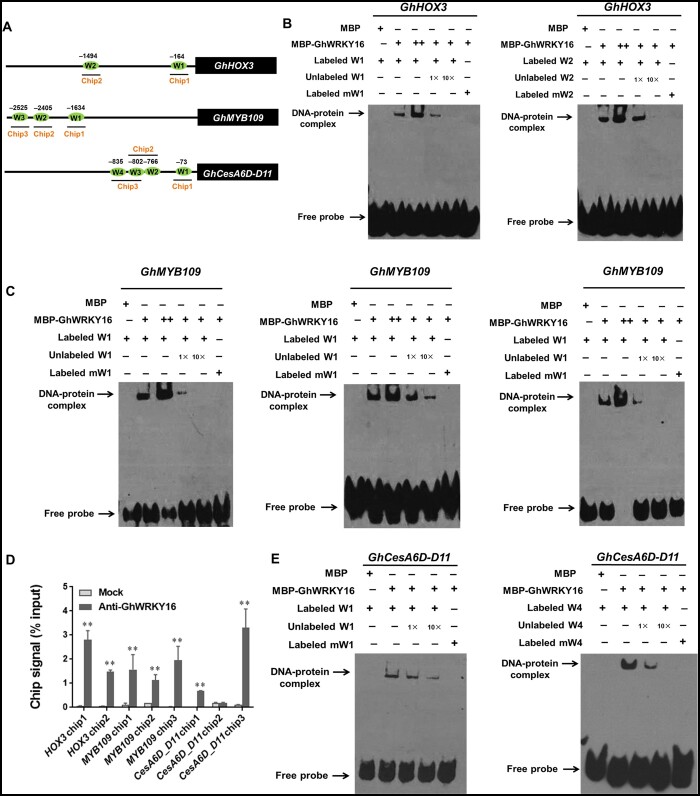
Figure 3.
GhWRKY16 binds to W-box cis-elements in the promoters of its target genes in vitro and in vivo. A, Schematic representation of W-box in GhHOX3, GhMYB109, and GhCesA6D-D11 promoters. Horizontal lines represent the promoters, green ovals represent W-boxes, and the line underneath indicates the fragments detected by ChIP-qPCR. B,C,E, EMSA of GhWRKY16 binding to the W-box in the promoters of GhHOX3 (B), GhMYB109 (C), and GhCesA6D-D11 (E). Biotin-labeled probes were incubated with MBP-GhWRKY16 in vitro. Unlabeled probes were used for competition, and biotin-labeled mutated W-box cis-elements (TTGAC to AAAAC) were used as negative controls. D, ChIP-qPCR analysis of GhWRKY16 binding to the GhHOX3, GhMYB109, and GhCesA6D-D11 promoters. An anti-GhWRKY16 polyclonal antibody was used for ChIP, followed by qPCR analysis of bound chromatin from 9 DPA cotton fibers. The ChIP signal is expressed as the percentage of immunoprecipitated DNA in the total input DNA. Mock, ChIP without anti-GhWRKY16 antibody. Error bars represent sd of three biological replicates. **P <0.01 by t-test between mock and anti-GhWRKY16 antibody