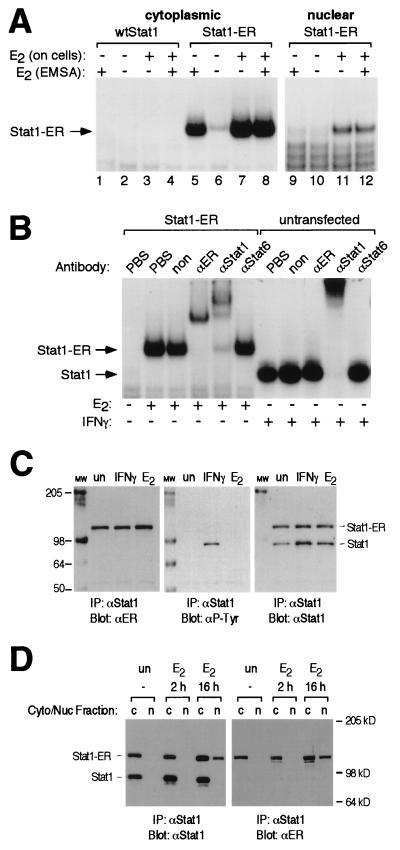
FIG. 3.
(A) In vitro DNA binding of the Stat1-ER chimera. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were prepared from Cos7 cells that had been either transfected with an expression vector driving the expression of Stat1-ER or left untransfected. Prior to the preparation of extracts, cells had either been left untreated or treated with estrogen (E2; 4 h). Extracts were analyzed by EMSA. In the indicated lanes, 1 μM estrogen (E2) was added directly to the EMSA reaction for 30 min. (B) Identification of shift complexes. Cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from Stat1-ER-transfected or untransfected Cos7 cells that had been treated as indicated. Extracts were incubated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), an irrelevant antibody (non), or antibodies specific for ER, Stat1, or Stat6 (αER, αStat1, or αStat6) and subjected to EMSA. The bands corresponding to the Stat1-ER chimera and wtStat1 are indicated. (C) Estrogen does not induce tyrosine phosphorylation of Stat1-ER. Whole-cell extracts from Stat1-ER-transfected Cos7 cells left untreated (un), treated with estrogen (E2; 4 h), or treated with IFN-γ (15 min) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with a Stat1 antibody. After resolution by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose, proteins were detected with the indicated antibodies (αP-Tyr, antiphosphotyrosine). The mobilities of molecular weight markers (lane MW; positions indicated in kilodaltons) and the bands corresponding to the Stat1-ER chimera and wtStat1 are indicated. (D) Estrogen induces nuclear translocation of the Stat1-ER chimera. Cytoplasmic (Cyto; lanes c) and nuclear (Nuc; lanes n) extracts prepared from Stat1-ER-transfected Cos7 cells left untreated (un) or treated with estrogen (E2; 2 h and 16 h) were immunoprecipitated with a Stat1 antibody. After resolution by SDS-PAGE and transfer to nitrocellulose, proteins were detected with the indicated antibodies. The mobilities of molecular weight markers and the bands corresponding to the Stat1-ER chimera and wtStat1 are indicated.