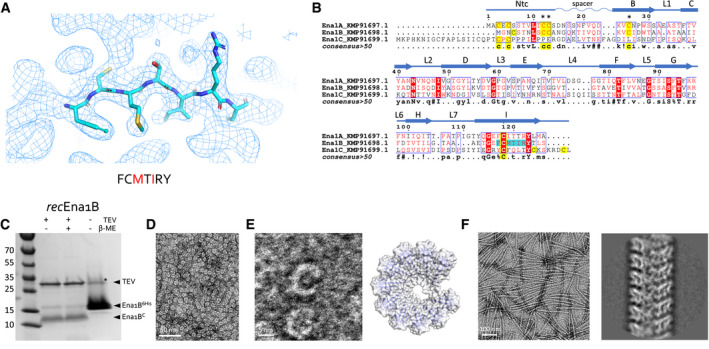
Figure 3. S‐Ena structure determination and recombinant production.
-
ARepresentative area of the 3D cryoEM potential map for ex vivo S‐Ena, at 3.2 Å resolution. An heptameric peptide with sequence FCMTIRY was deduced de novo from the cryoEM potential map (shown in sticks) and used for a BLAST search of the B. cereus NVH 0075‐95 genome. The red letters indicate amino acids that differ between KMP91697.1 and KMP91698.1 (see B).
-
BMultiple sequence alignment of 3 ORF’s (KMP91697.1, KMP91698.1, and KMP91699.1) corresponding to DUF3992 containing proteins. Sequence motifs corresponding or similar to that deduced from the EM potential map are shaded in cyan. Secondary structure and structural elements as determined from the built model (see Fig 2) are shown schematically above the sequences (Ntc: N‐terminal connecter; arrows correspond to β‐strands, labeled as in Fig 2). Contiguous areas of >50% similarity are boxed blue.
-
CSDS–PAGE of recEna1B, treated with β‐mercaptoethanol or TEV protease (to remove N‐terminal 6xHis tag) as indicated. Bands with apparent MW of ˜13 and ˜15 kDa correspond recEna1B monomer with (Ena1B6His) and without (Ena1BC) the 6xHis tag and TEV recognition site, respectively. In the uncleaved sample, a band running at ˜30 kDa (labeled *) corresponds to a non‐physiological disulfide bound S‐Ena1B dimer. Lower intensity in the cleaved recEna1B results from a loss of monomers to SDS‐resistant high‐molecular‐weight complexes stuck in the stacking gel.
-
DNegative stain TEM images of rec1Ena1B oligomers formed after refolding, but prior to TEV removal of the N‐terminal 6xHis tag.
-
EClose‐up view that shows recEna1B oligomers form open crescents similar in dimensions and shape to single helical turns or arcs found in the S‐Ena fiber (model – right). Steric hindrance by the 6xHis is thought to arrest recEna1B polymerization into single helical arcs.
-
FNegative stain image and 2D classification of S‐Ena‐like fibers formed after TEV digestion of recEna1B. Upon removal of the N‐terminal 6xHis tag, recEna1B readily assembles into fibers with helical properties closely resembling those found for ex vivo S‐Enas.
