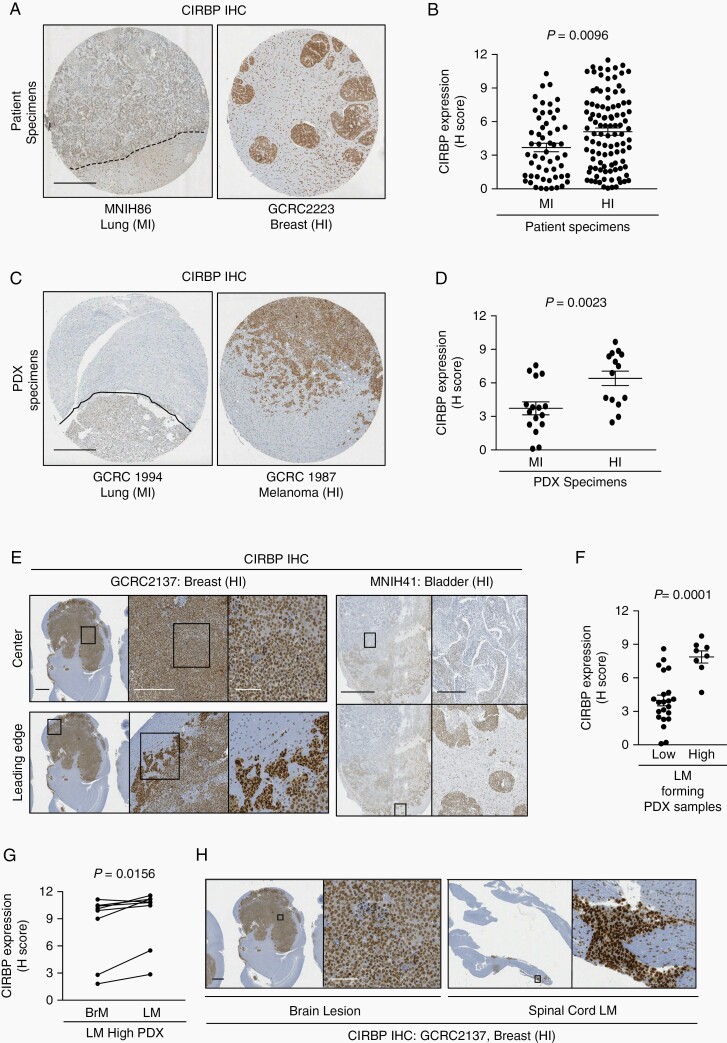
Fig. 4.
CIRBP is associated with HI invasion pattern in BrM. CIRBP expression in MI and HI BrM from a tissue micro-array of A and B, patient specimens; C and D, PDX models. Representative images of MI (left) and HI (right) lesions shown in A and C. Dotted lines represent the well-demarcated margin in MI lesions. Scale bars: 500 µm. Quantification of staining shown in B and D. H-Score was calculated as a score out of 12 that encompasses percentage positivity and staining intensity by the following formula: (% positivity/25) × ((1× % of 1+ cells) + (2× % of 2+ cells) + (3× % of 3+ cells)). Statistical analyses were performed using a two-sided Mann-Whitney test. E, Representative examples demonstrating overexpression of CIRBP at the leading edge of parenchymal brain lesion in a PDX model (left) and patient specimen (right). Scale bars: 1 mm, 500 µm, 100 µm and 5 mm, 500 µm, respectively. F, CIRBP expression in low- and high-LM-forming PDX models. Statistical analyses were performed using a two-sided Mann-Whitney test. G, Fold-change comparing CIRBP H-score in spinal cord LM compared to parenchymal BrM in high-LM-forming PDX models. Statistical analyses were performed using a two-sided Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. H, Representative example demonstrating overexpression of CIRBP in spinal cord LM compared to parenchymal brain lesion. Scale bars: 1 mm, 100 µm. Abbreviations: BrM, brain metastases; CIRBP, cold-inducible RNA-binding protein; HI, highly invasive; MI, minimally invasive; LM, leptomeningeal metastases; PDX, patient-derived xenografts.