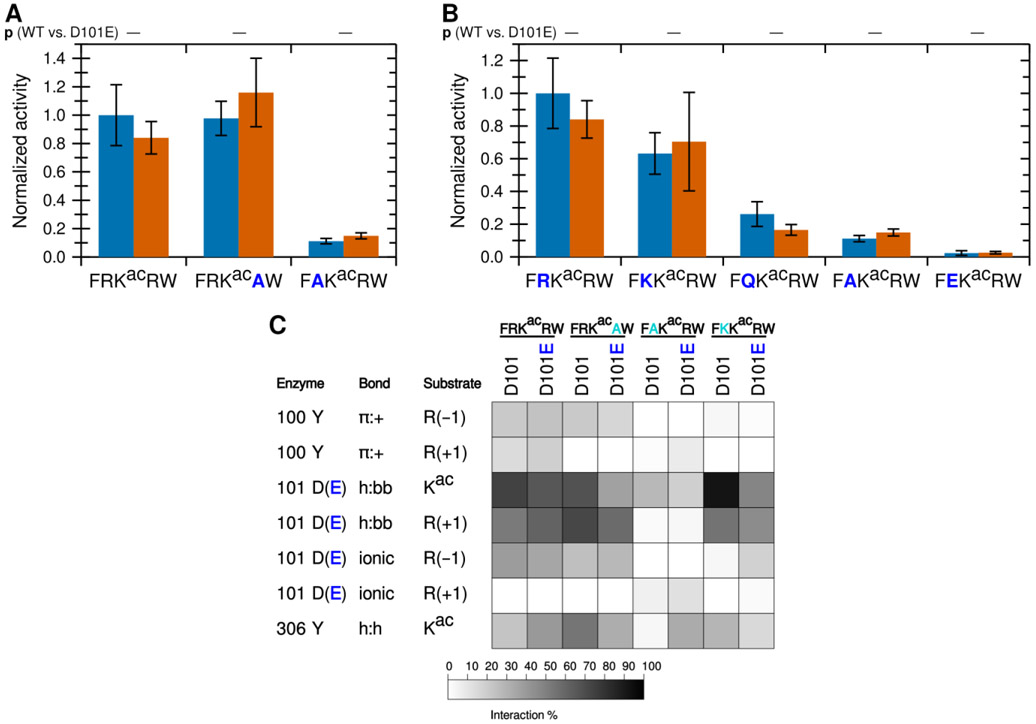
Figure 5. KDAC8 D101E is equivalent to wild-type KDAC8.
(A) Wild-type KDAC8 (blue) or KDAC8 D101E (red) with FRKacRW and derivative peptides containing arginine to alanine substitutions. Average specific activity was normalized such that the activity of wild-type KDAC8 with FRKacRW was represented as 1. Error bars represent standard deviations (n≥4). No statistically significant differences exist between WT and KDAC8 D101E. (B) Wild-type KDAC8 (blue) or KDAC8 D101E (red) with FRKacRW and derivative peptides containing substitutions at the −1 position. Data are represented as in panel A. Blue bars in panels A and B are the same data presented in Figures 2 and 3, reproduced here to allow comparison. No statistically significant differences exist between WT and KDAC8 D101E. (C) Results of MD analysis comparing interactions between residues of wild-type KDAC8 or KDAC8 D101E and a subset of peptide substrates reacted in panels A and B. Shading corresponds to the percent of time a particular interaction was observed during MD simulations.