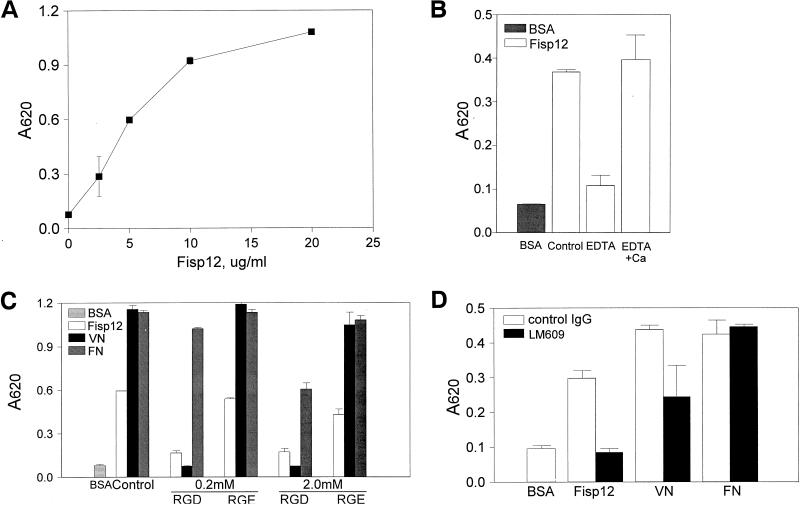
FIG. 1.
Fisp12 mediates HMVEC adhesion through integrin αvβ3. HMVECs were washed and harvested in PBS with 1 mM EDTA, resuspended in serum-free medium, and plated on microtiter wells coated with indicated substrates. After incubation at 37°C for 30 min, adherent cells were fixed and stained with methylene blue, followed by quantitation by measuring the absorbance at 620 nm. Data shown are the means of duplicate determinations, and similar results were obtained in at least three separate experiments. Error bars represent the standard deviation(s) (SD). (A) Dose dependence of adhesion to Fisp12. HMVECs were plated onto microtiter wells coated with the indicated concentrations of purified Fisp12. (B) Divalent cation dependence. HMVEC adhesion to either BSA- or Fisp12-coated plates was determined; EDTA (10 mM) or Ca2+ (20 mM) was added where indicated. (C) Inhibition by RGD peptides. HMVECs were incubated with either buffer (control) or 0.2 or 2.0 mM GRGDSP or GRGESP peptides, as indicated, prior to addition to the microtiter wells coated with Fisp12 (5 μg/ml), 2 μg of fibronectin per ml (FN), or 0.1 μg of vitronectin per ml (VN). (D) HMVEC adhesion to Fisp12 was dependent on integrin αvβ3. Microtiter wells were coated with BSA, Fisp12 (2.5 μg/ml), fibronectin (2 μg/ml), or vitronectin (0.1 μg/ml). HMVECs were incubated with either normal mouse immunoglobulin G or the anti-αvβ3 antibody LM609 (50 μg/ml) prior to plating, and adhesion was measured at 30 min thereafter.