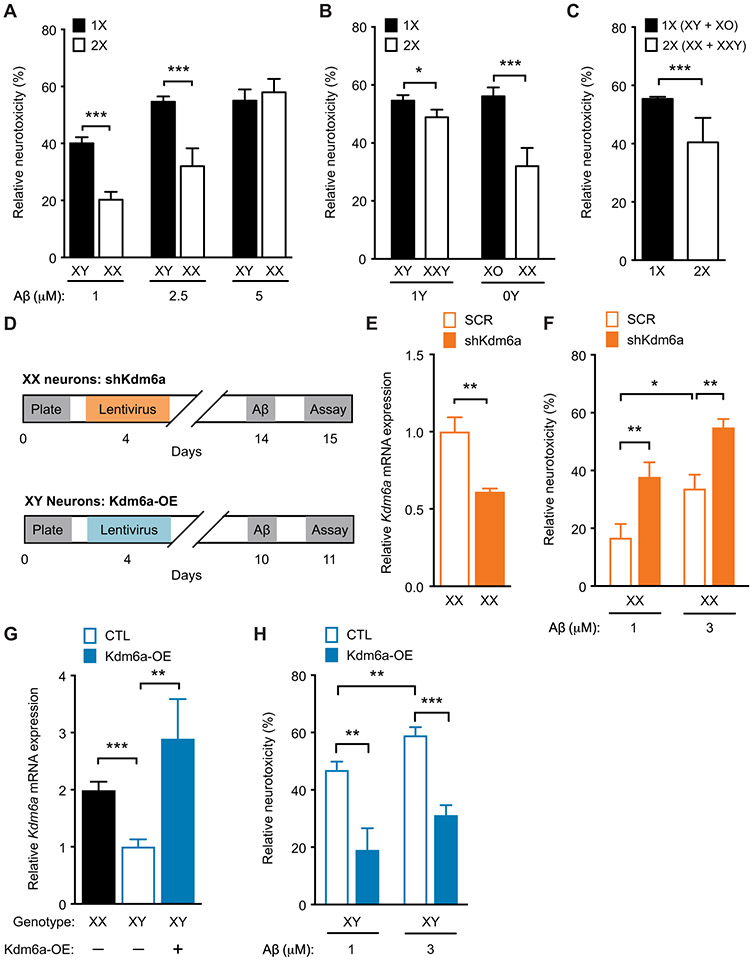
Fig. 7. Kdm6a knockdown in XX mouse neurons worsens, whereas Kdm6a overexpression in XY neurons attenuates Aβ toxicity in vitro.
(A to C) Vulnerability of mouse primary neurons was tested by the MTT assay. For each genotype, cell toxicity was calculated as a percentage of the corresponding vehicle-treated group, 24 hours after treatment with increasing doses of Aβ. (A) Mouse primary cortical XY neurons showed greater vulnerability than did XX neurons after exposure to vehicle or increasing doses of Aβ (n = 8 to 40 wells per experimental group from 8 to 10 pups per genotype, from four independent litters). Two-way ANOVA: sex chromosome effect, P < 0.01; Aβ dose effect, P < 0.001; interaction, P < 0.05. (B) Toxicity of Aβ in neurons of varying X and Y chromosome dosage derived from littermate pups of XY* males crossed with nontransgenic (NTG) females, with genotypes roughly equivalent to XO, XX, XY, and XX, exposed to vehicle or Aβ (2.5 μM) (n = 15 to 45 wells per experimental group from 7 to 10 pups per genotype, from four independent litters). Two-way ANOVA: X effect, P < 0.0001; Y effect, not significant; X by Y interaction, P < 0.05. (C) Main effect of X chromosome dose shows increased Aβ toxicity in neurons with 1X (XO and XY combined) compared to those with 2X chromosomes (XX and XXY combined). (D) Experimental strategy of lentivirus-mediated knockdown of Kdm6a in XX mouse primary cortical neurons (top) and Kdm6a overexpression in XY mouse primary cortical neurons (bottom). (E) Shown is Kdm6a mRNA expression in neurons transfected with lentivirus expressing scrambled (SCR) or short hairpin (sh) Kdm6a for knockdown expressed relative to XX SCR (n = 5 to 6 wells per experimental group from eight XX pups, from two litters). Two-tailed t test, **P < 0.01. (F) Shown is Aβ toxicity in XX neurons treated with SCR or shKdm6a and exposed to vehicle or Aβ (1 and 3 μM); knockdown of Kdm6a worsened Aβ toxicity (n = 24 to 25 wells per experimental group from 14 XX pups, from three independent litters). Two-way ANOVA: Kdm6a effect, P < 0.001; Aβ effect, P < 0.001; Kdm6a by Aβ interaction, P = 0.99. (G) Kdm6a mRNA expression in neurons transfected with lentivirus expressing control (CTL) or overexpressing Kdm6a (Kdm6a-OE), shown relative to control XY neurons (n = 3 to 8 wells per experimental group from 12 XY pups, from two independent litters). One-way ANOVA, P < 0.001. (H) Shown is Aβ toxicity in XY neurons transfected with lentivirus expressing control or overexpressing Kdm6a (Kdm6a OE) and exposed to vehicle or Aβ (1 and 3 μM); overexpression of Kdm6a attenuated Aβ toxicity (n = 12 to 13 wells per experimental group from 26 XY pups, from three independent litters). Two-way ANOVA: Kdm6a effect, P < 0.001; Aβ effect, P = 0.01; Kdm6a by Aβ interaction, P = 0.99. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 (Bonferroni-Holm). Data are presented as means ± SEM.