FIGURE 3.
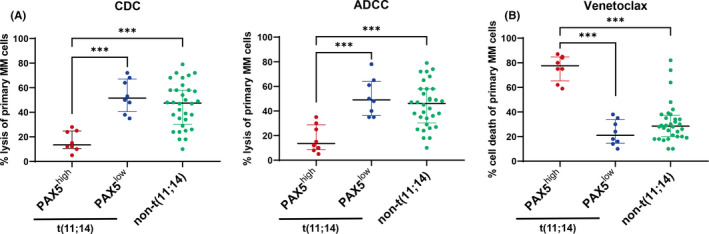
Patients with t(11;14) expressing B–cell‐associated genes are less sensitive to daratumumab‐induced direct cytotoxicity but highly sensitive to venetoclax. Asterisks denote significant changes (*.01 ≤ P < .05, **.001 ≤ P < .01, and ***P < .001); ns, not significant. ADCC, antibody‐dependent cellular cytotoxicity; BM‐MNC, bone marrow mononuclear cells; CDC, complement‐dependent cytotoxicity. A, Ex vivo CDC and ADCC assays using primary myeloma samples. BM‐MNCs from 48 patients with newly diagnosed MM were used in ADCC and CDC assays with 10 μg/ml daratumumab. ADCC and CDC assays were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Bars indicate the median with interquartile range. Significance was assessed by Kruskal‐Wallis test. B, Flow cytometry‐based ex vivo cell death assay in primary myeloma cells treated with venetoclax. BM‐MNCs from 48 patients with newly diagnosed MM were treated with 300 nM venetoclax or vehicle control (DMSO) for 24 h. Myeloma cells were identified by CD138 staining. Cell death was measured as the loss of CD138 staining. The percentage of venetoclax‐mediated cell death was calculated using the following formula: % cell death = 1 − (absolute number of surviving CD138+ cells in the presence of venetoclax/absolute number of surviving CD138+ cells in the presence of DMSO control) × 100%
