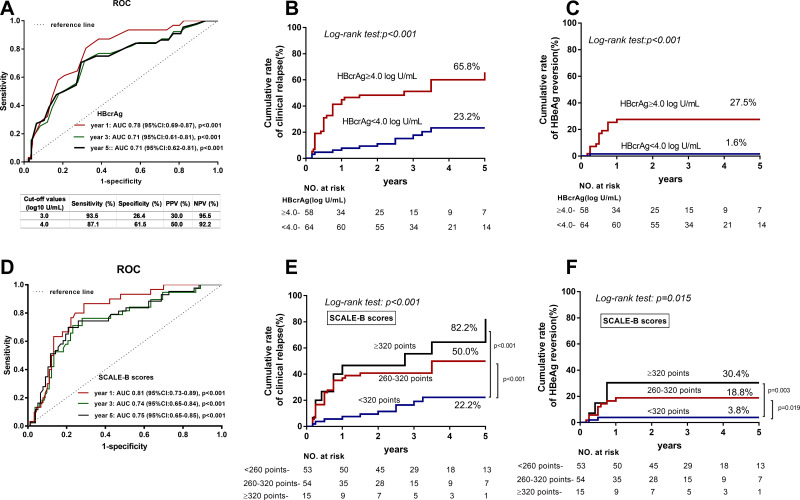
Figure 2.
ROC curves of HBcrAg and SCALE-B scores to predict clinical relapse after discontinuation of NA therapy. (A) Respective AUCs of HBcrAg for predicting of clinical relapse after NA discontinuation at 1, 3, and 5 years were 0.78 (p < 0.001), 0.71 (p < 0.001) and 0.71 (p<0.001). (B) In stratification analysis EOT HBcrAg level ≥ 4.0 log10 U/mL was associated with a higher risk of clinical relapse (65.8% vs 23.2%, p < 0.001). (C) EOT HBcrAg level ≥ 4.0 log10 U/mL was associated with a higher risk of HBeAg reversion (27.5% vs 1.6%, p < 0.001). (D) Respective AUCs of SCALE-scores for predicting of clinical relapse after NA discontinuation at 1, 3, and 5 years were 0.81 (p < 0.001), 0.74 (p < 0.001) and 0.75 (p<0.001). (E) SCALE-B score < 260 points (22.2%) was associated with a lower risk of clinical relapse, compared to 260–320 points (50%, p < 0.001) and ≥ 320 points (82.2%, p < 0.001). (F) SCALE-B score < 260 points (3.8%) was associated with a lower risk of HBeAg reversion, compared to 260–320 points (18.8%, p < 0.001) and ≥ 320 points (30.4%, p < 0.001).