FIGURE 1.
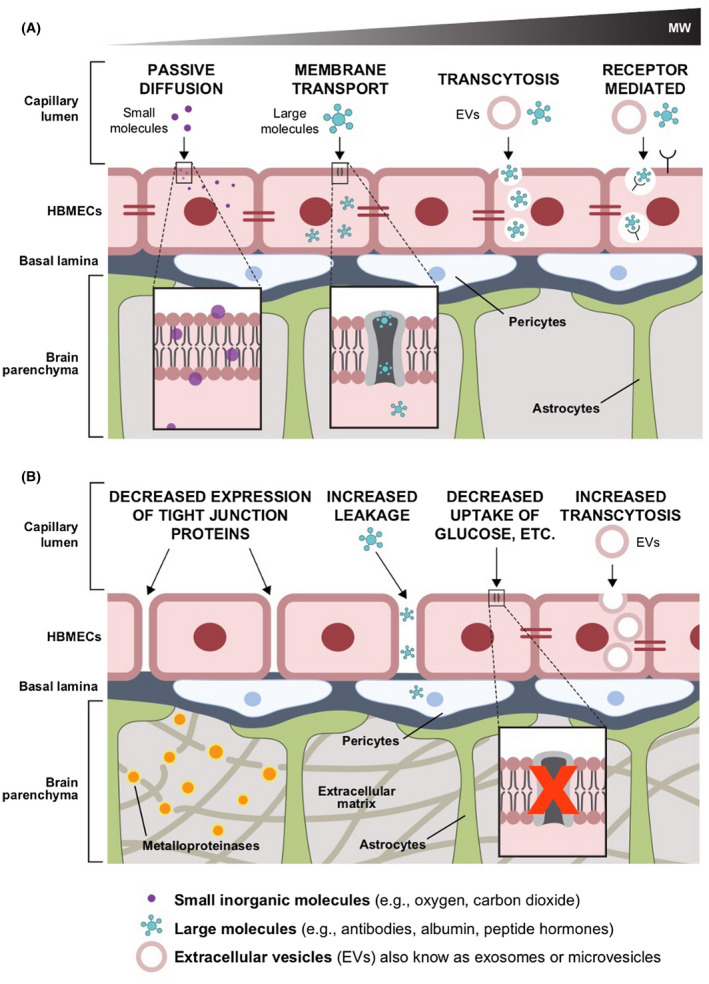
Examples of pathways and mechanisms of transport at the blood–brain barrier during (A) physiological conditions (e.g., passive diffusion, receptor‐mediated transcytosis) and (B) pathological processes, such as primary and metastatic brain cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases (e.g., decreased expression of tight junction proteins, increased paracellular leakage, decreased expression of membrane protein for active transport of molecules, and increased cancer‐extracellular vesicle [EV] transcytosis)
