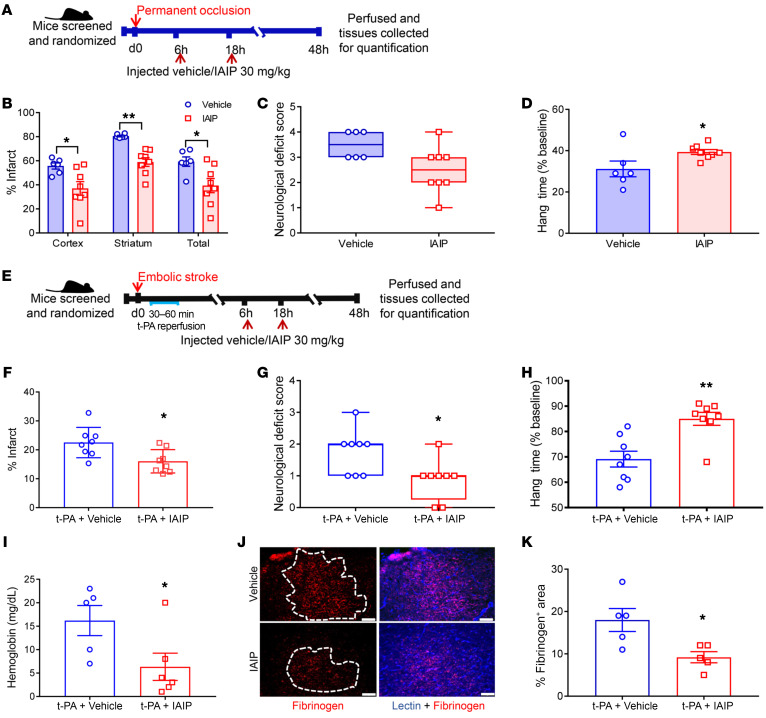
Figure 6. IAIP treatment confers significant protection in both a permanent occlusion model and a thromboembolic stroke model.
(A) Young male mice were subjected to permanent MCAO followed by treatment with IAIP or vehicle. (B) Infarct quantification after permanent MCA occlusion showed neuroprotection in the cortex (*P = 0.0185), striatum (**P = 0.0054), and total hemisphere (*P = 0.0111) at 48 hours after stroke with IAIP compared with the vehicle group by 2-sample t tests adjusted for multiple testing. (C) NDS 24 hours after stroke with IAIP and vehicle treatment (P = 0.0706, Wilcoxon’s rank sum test). (D) IAIP-treated mice had a significantly longer latency to fall in the grip test 48 hours after stroke (*P = 0.0378, t test). (E) Young male mice subjected to embolic stroke followed by t-PA administration were randomly assigned to IAIP or vehicle treatment as shown in the timeline. (F) Mice that received IAIP in combination with t-PA had reduced infarct compared with mice treated with t-PA and vehicle after thromboembolic stroke (mean ± SEM; *P = 0.0290, 2-sample t test). (G) Mice treated with t-PA plus IAIP after thromboembolic stroke demonstrated a significantly improved NDS 24 hours after stroke (*P = 0.046, Wilcoxon’s rank sum test). (H) IAIP-treated mice had a longer latency to fall in the hang-wire test 48 hours after stroke (**P = 0.0015, t test). (I) Mice that received IAIP had significantly reduced hemoglobin levels in the ipsilateral hemisphere (*P = 0.0487, t test). (J) Representative immunohistochemistry images analyzed 48 hours after thromboembolic stroke showed that IAIP reduced BBB leakage, as seen by fibrinogen immunoreactivity (red), counterstained with lectin (blue). Scale bars: 75 μm. (K) Quantification of fibrinogen immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral hemisphere of mice treated with t-PA plus IAIP compared with vehicle-treated mice (mean ± SEM; *P = 0.0196, t test).