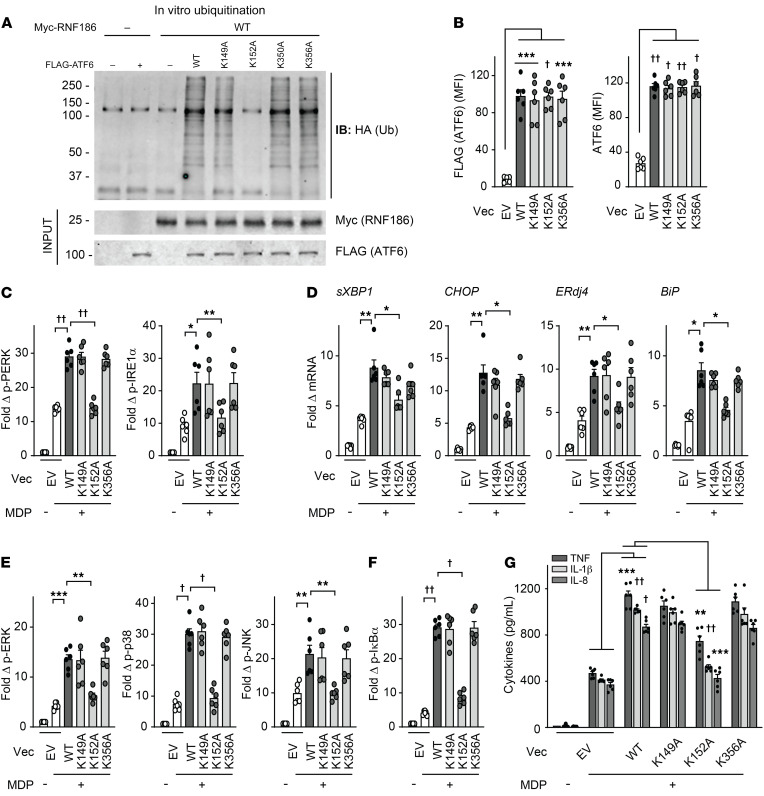
Figure 5. Lysine 152 in ATF6 is critical for RNF186-dependent ubiquitination of ATF6 and PRR-induced, RNF186-dependent downstream outcomes.
(A) In vitro ubiquitination was assessed as per Methods with purified HA-ubiquitin with/without purified myc-RNF186 WT with/without purified FLAG-tagged WT or lysine mutants (K149A, K152A, K350A, K356A) of ATF6. Ubiquitin protein (α-HA) was detected by Western blot (representative of 3 independent experiments). Marker positions are shown (kDa). (B–G) MDMs were transfected with empty vector (EV) or FLAG-tagged WT or mutants of ATF6. (B) ATF6 protein expression as detected by flow cytometry (n = 6). (C–G) Transfected MDMs (n = 6) were treated with 100 μg/mL MDP. (C) Fold phospho-PERK and phospho-IRE1α induction at 30 minutes. (D) Fold change mRNA expression at 4 hours. (E and F) Fold phospho-protein induction at 15 minutes. (G) Cytokines at 24 hours. Similar results in an additional n = 6 for B–G. Mean + SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; †P < 1 × 10−4; ††P < 1 × 10−5 determined by 2-tailed Student’s t test with a Bonferroni-Holm correction for multiple comparisons. Vec, vector.