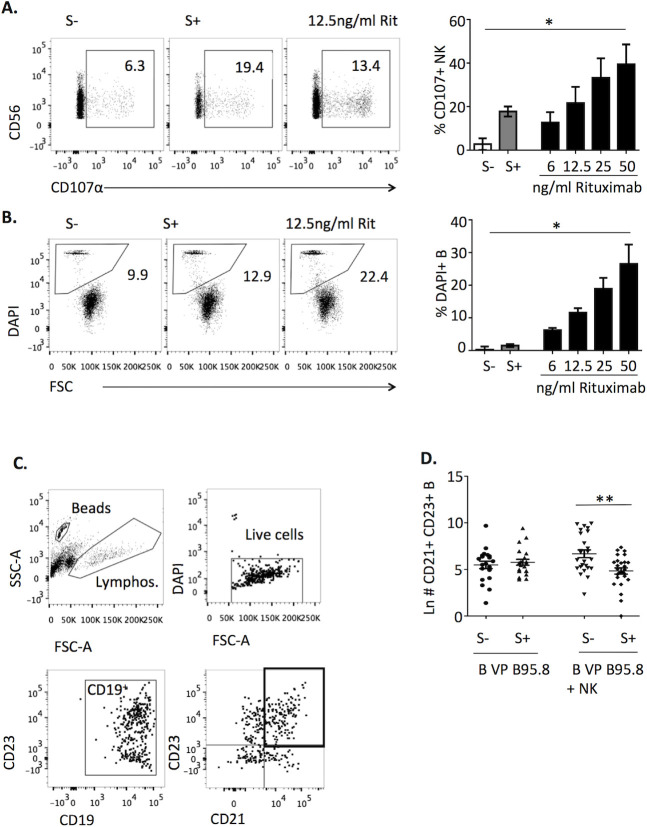
Fig 1. Interaction of NK cells with B cell-bound EBV VP in the presence of EBV S+ reduces transformation without inducing B cell death.
(A, B) B cells were stained with fluorescent dye, coated with B95.8 VP for 1h at 4°C, washed, and cultured with autologous NK cells in the presence of EBV S-, EBV S+ serum or the indicated doses of Rituximab. After 4h, the percentages of CD107α+ NK cells (A) and of DAPI+ B cells (B) were determined by flow cytometry. Background levels without B cells (for CD107α) or without NK cells (for DAPI) were substracted. Plots of a representative experiment (left) and results of three (right) are shown. Statistical analysis was performed with Friedman test with Dunn’s post-test. (C, D) B cells were incubated with B95.8 VP for 1h at 4°C, washed and cultured alone or with autologous NK cells in the presence of EBV S- or S+ serum for 4h. Subsequently, B cells separated from NK cells were plated at 50,000 cells /well, cultured for 2 weeks and stained for CD19, CD21, CD23 and DAPI. (C) Representative gating strategy. (D) Data are expressed as Ln of the number of live CD23+ CD21+ CD19+ cells detected in 20–26 wells per condition from 3 experiments. Statistical analysis was performed with one-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test.