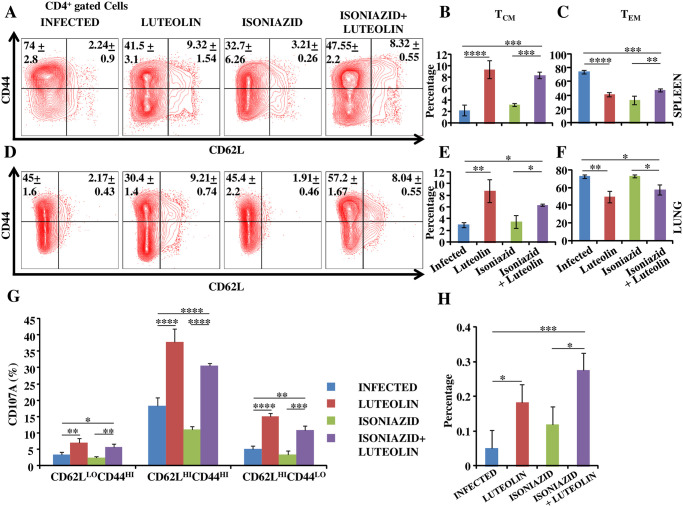
Fig 3. Luteolin induces superior antigen-specific memory T cell responses.
T lymphocytes isolated from lungs and spleens of the indicated groups of experimental mice at 60 days post-infection were surface-stained with anti-CD3, -CD4, -CD44, -CCR7 and -CD62L antibodies on ice and fixed prior to acquisition by flow cytometry. Representative FACS profile (A) and proportion of central memory (B) and effector memory (C) subsets of CD4+ T cells in spleen. Representative FACS profile (D) and proportion of central memory (E) and effector memory (F) subsets of CD4+ T cells in lung. (G) Ex-vivo M.tb CSA antigen-specific degranulation in different CD4+ T cell subsets in lung. (H) Multifunctional CD4+ T cell populations in lung of infected, Luteolin-treated, Isoniazid-treated and Luteolin+Isoniazid-treated mice. Data shown here are representative of three independent experiments with three mice in each group and represent the MEAN±STDEV values. Differences were considered significant at P<0.05 and are represented by * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001 whereas non-significant differences are denoted by (NS).