Figure 1. IL-6 deficient (IL-6−/−) mice have similar kidney function and injury after sham (surgery alone), ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) or bilateral nephrectomy (BNx).
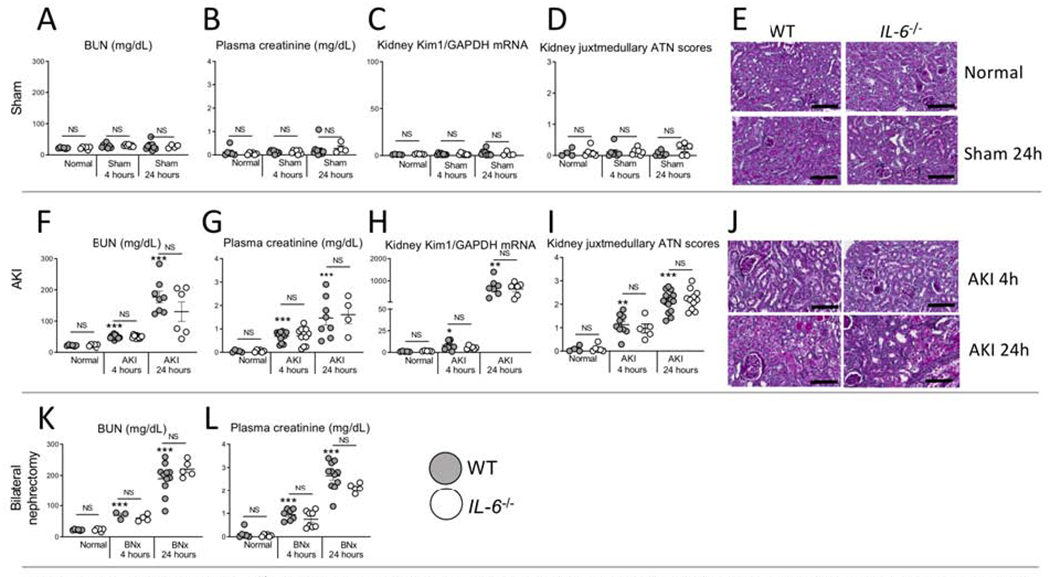
Kidney injury was determined in normal (unmanipulated) mice, and after sham, AKI or BNx at 4 and 24 hours in wild type (WT) and IL-6−/− mice. No kidney injury occurred after sham (surgery alone) in either WT or IL-6−/− as judged by (A) BUN, (B) plasma creatinine, (C) kidney KIM-1 mRNA, and (D) ATN score with (E) representative PAS images. Kidney injury was similar at 4 and 24 hours after AKI between WT and IL-6−/− mice as judged by (F) BUN, (G) plasma creatinine, (H) kidney mRNA KIM-1, and (I) ATN scores with (J) representative PAS images. Wild type and IL-6−/− mice with bilateral nephrectomy had similar levels of (K) BUN and (L) plasma creatinine. N=3 to 12 mice per group from 3 experiments. Results are expressed as mean ±SEM and analyzed by t test: WT versus IL-6−/− at the same time point (indicated above the bar) and versus normal WT (indicated below the bar: *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P < 0.0001). Scale bar: 100 μm.
