Figure 4. NGAL protein accumulates in the liver, lung, spleen, and kidney at 4 and 24 hours after sham (surgery alone), ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI) or bilateral nephrectomy (BNx).
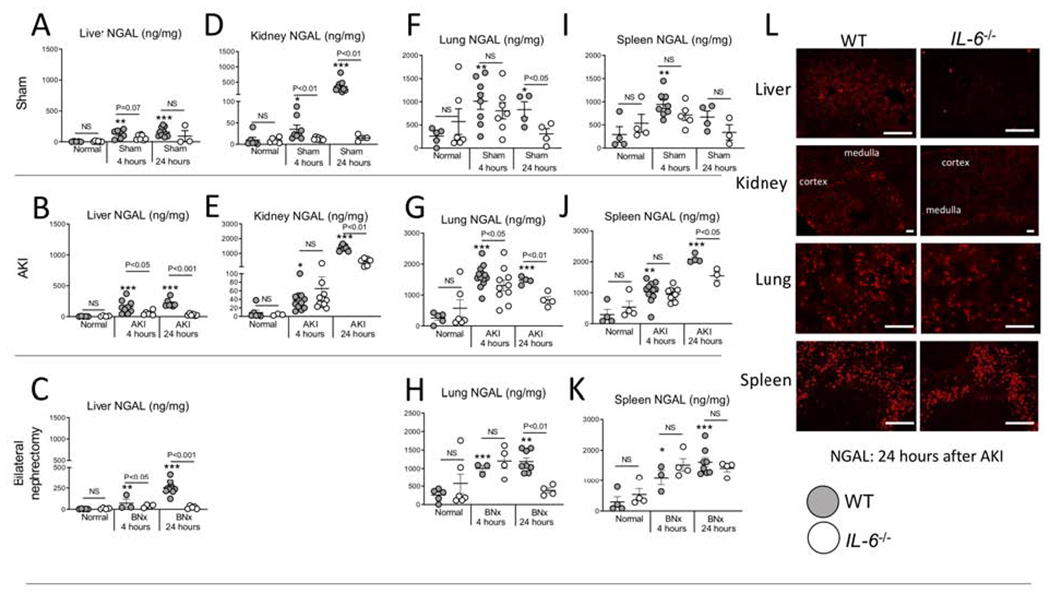
NGAL protein levels (ELISA) were determined in normal (unmanipulated) mice, and 4 and 24 hours after sham, AKI and BNx in wild type (WT) and IL-6−/− mice in the (A-C) liver, (D-E) kidney, (F-H) lung, and (I-K) spleen. (L) Immunofluorescence staining for NGAL was performed 24 hours after AKI in WT and IL-6−/− in the liver, kidney, lung, and spleen (representative images). N=3 to 12 mice per group from 3 experiments. Results are expressed as mean ±SEM and analyzed by t test: WT versus IL-6−/− at the same time point (indicated above the bar) and versus normal WT (indicated below the bar: *P<0.05; **P<0.01, ***P < 0.0001). Scale bar: 100 μm.
