Figure 6. Intravenous (IV) administration of IL-6 to normal WT mice induces NGAL production (mRNA) in the liver and increases plasma NGAL.
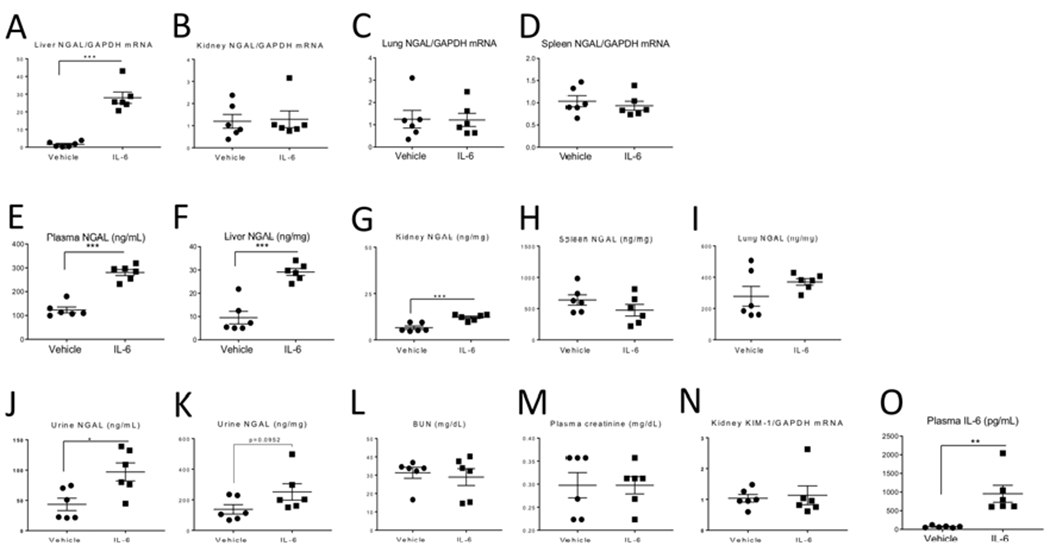
200 ng of recombinant murine IL-6 or 0.1% BSA was administered IV every hour for 3 hours to healthy WT mice; endpoints were determined 1 hour after the last IV injection. mRNA NGAL expression was significantly increased in the (A) liver, but not the (B) kidney, (C) lung, or (D) spleen in IL-6-treated. Protein NGAL levels were significantly increased in the (E) plasma, (F) liver, and (G) kidney but not the (H) spleen, or (I) lung in IL-6-treated. Urine NGAL was significantly increased (J), but not when corrected for urine creatinine (K) in IL-6-treated. Kidney injury did not occur after IL-6 administration as judged by similar levels of (L) BUN, (M) plasma creatinine and (N) kidney KIM-1 mRNA expression. (O) Plasma levels of IL-6 were increased in mice receiving IV IL-6, as expected. Data were analyzed by t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, Vehicle vs IL-6. Results are expressed as mean ±SEM of expression values for 6 mice per group from 1 experiment, n=6).
