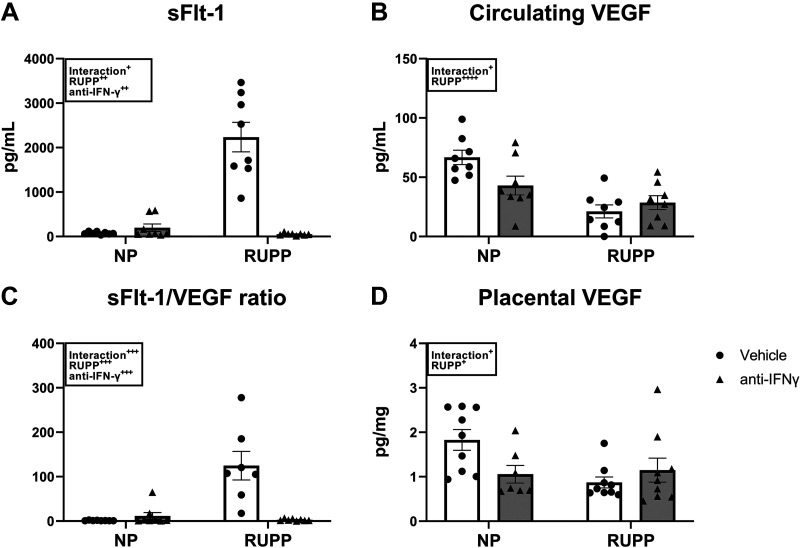
Figure 3.
Effect of interferon γ (IFNγ) neutralization on circulating and placental angiogenic factors. On gestation day (GD) 14, the reduced uterine perfusion pressure (RUPP) procedure was performed on a subset of normal pregnant (NP) rats. On GDs 15 and 18, vehicle or 10 μg/kg of anti-IFNγ antibody was injected intraperitoneally in a subset of NP and RUPP rats. On GD 19, blood and placentas were collected under isoflurane anesthesia and processed for further analysis. Circulating soluble Fms-Like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1; A) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF; B) were measured via ELISA and the sFlt-1-to-VEGF ratio (C) is shown. Placental VEGF (D) was measured using the Bio-Plex Pro Rat Cytokine Immunoassay Kit. NP: n = 8–9 rats; RUPP: n = 8–9 rats; NP + anti-IFNγ: n = 7–9 rats; RUPP + anti-IFNγ: n = 8–9 rats. All data are expressed as means ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. +P < 0.05; ++P < 0.01; +++P < 0.001; ++++P < 0.0001.