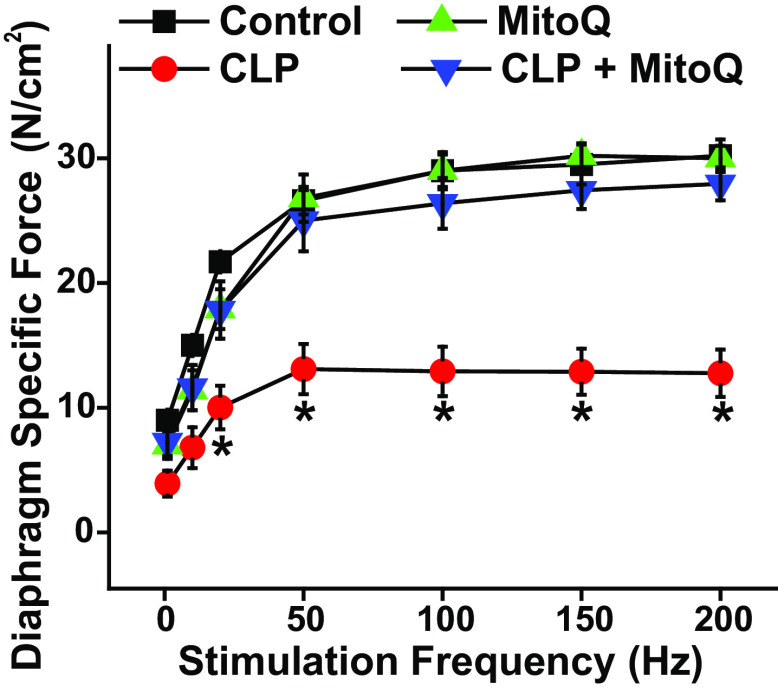
Figure 1.
MitoQ administration ablates sepsis-induced diaphragm weakness. Diaphragm specific force generation (i.e. force per cross-sectional area) in response to increasing stimulation frequencies (n = 5 or 6 animals/group) is shown for sham (black), sham + MitoQ (green), CLP (red), and CLP + MitoQ (blue) groups. CLP induced large reductions in diaphragm force generation in response to 20–200-Hz excitation frequencies when compared with values for sham-operated control animals (P < 0.01 for comparison at each frequency). MitoQ treatment prevented CLP-induced reductions in force, with diaphragm specific force for the CLP + MitoQ group higher than CLP values (P < 0.02 for 20–200 Hz). Force levels for the sham + MitoQ group were similar to those in the sham controls (NS). Data are presented as mean values with error bars representing 1 standard error of the mean. ANOVA was used to compare variables across groups; *statistical significance. CLP, cecal ligation puncture; MitoQ, mitoquinone mesylate.