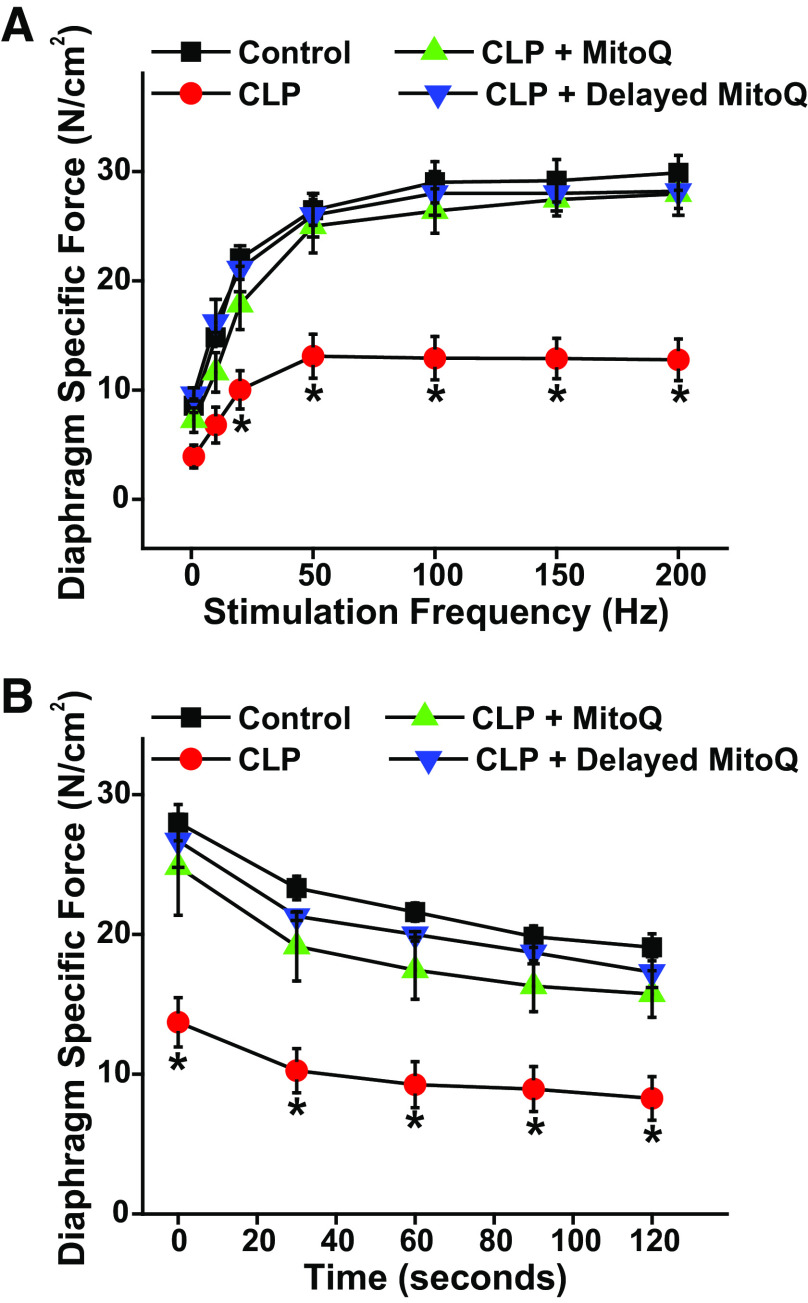
Figure 7.
Delayed MitoQ administration preserves diaphragm function in CLP sepsis. Data compare the efficacy of delayed administration of MitoQ (6 h after CLP surgery) to the effects of immediate administration of MitoQ (at the time of CLP surgery) (n = 4 or 6 animals/group). A presents diaphragm mean force-frequency curves and B shows diaphragm force over time during repetitive contraction trials. Delayed MitoQ administration was as effective as immediate administration in preventing CLP-induced reductions in diaphragm specific force generation (P < 0.001 for both immediate MitoQ + CLP and delayed MitoQ + CLP as compared with the CLP group for 20–200 Hz stimulation frequencies). Delayed and immediate MitoQ also had similar effects on diaphragm force during repetitive contraction trials (P < 0.02 for both groups compared with the CLP group at all time points). Data are presented as mean values with error bars representing 1 SE of the mean. ANOVA was used to compare variables across groups treated with different agents; *statistical significance. CLP, cecal ligation puncture; MitoQ, mitoquinone mesylate.