Figure 1.
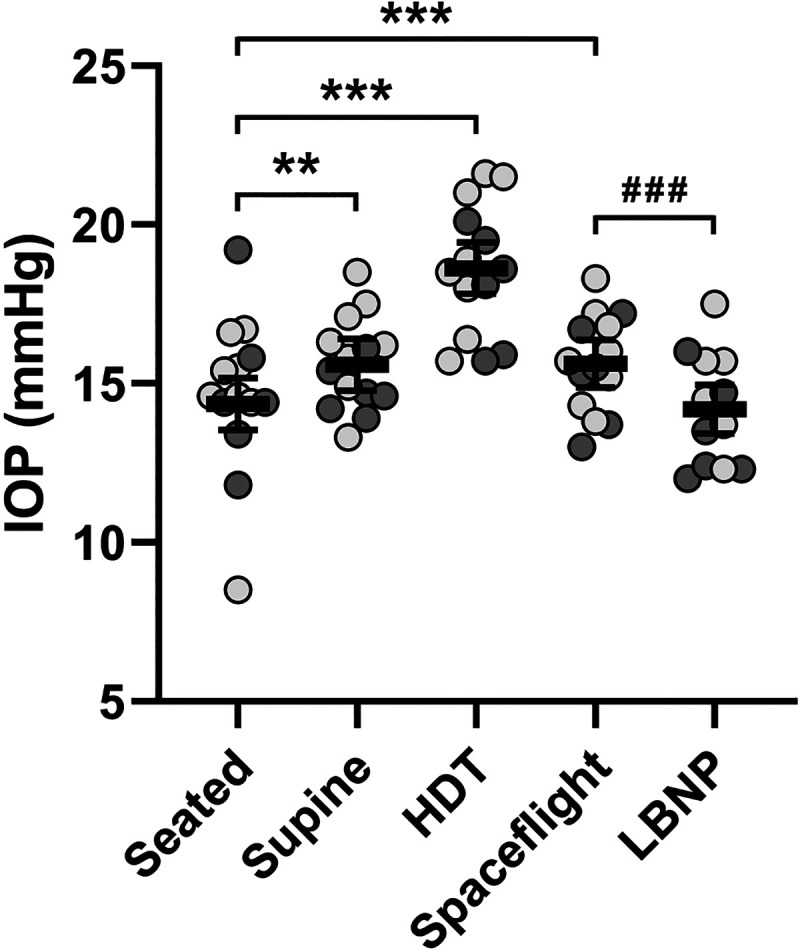
Reduction of intraocular pressure by LBNP-induced acute fluid shifts during spaceflight. IOP elevates with acute, head-lowering posture changes on Earth. In comparison with the seated posture, long-duration spaceflight results in a mild elevation of IOP that can be countered with acute application of LBNP. Mean values (bars) of individual subject left eye data (light circles, no prior spaceflight experience; dark circles, prior spaceflight experience) are shown, and error bars represent 95% CI; n = 14 subjects. Statistical significance is indicated by **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 for comparison to the seated posture and by ###P < 0.001 for comparison to the LBNP condition (mixed model analysis). CI, confidence interval; HDT, head-down tilt; IOP, intraocular pressure; LBNP, lower body negative pressure.
