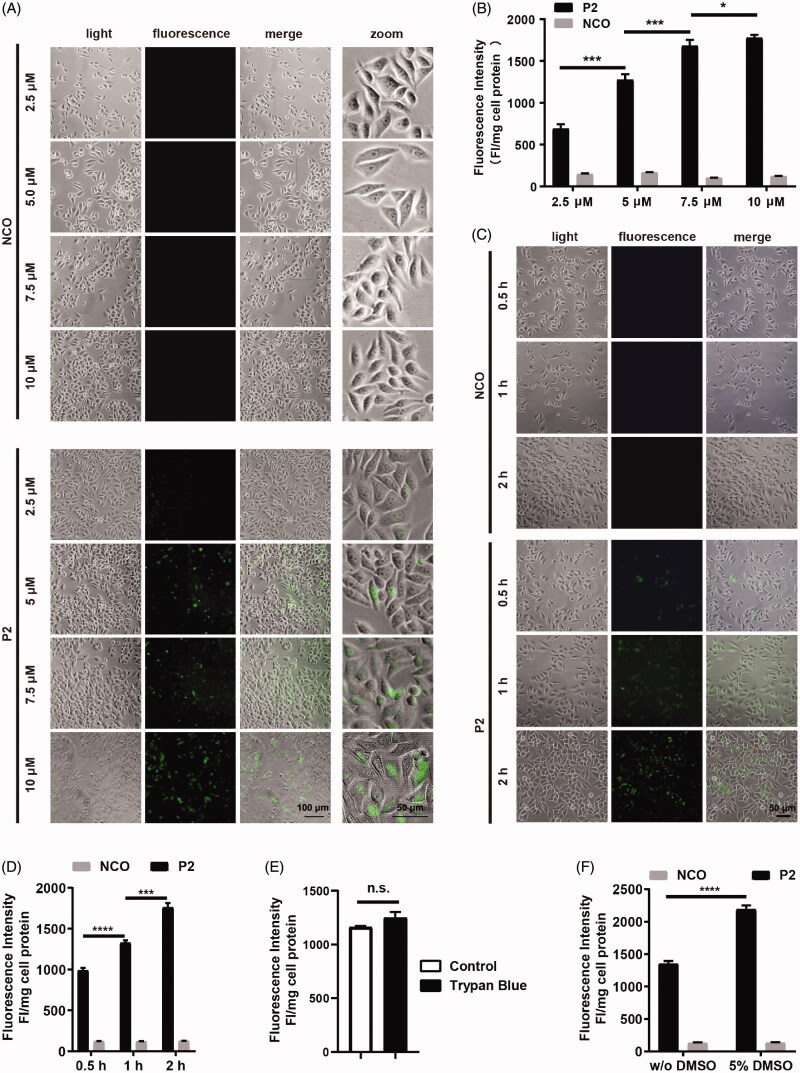
Figure 3.
Cellular uptake of peptide P2. (A) Fluorescence microscopy images of FITC-labeled peptide P2 at indicated concentrations for 1 h. (B) Fluorescence intensity quantification of FITC-labeled peptide P2 at indicated concentrations for 1 h. Fluorescence intensity was normalized by protein concentration of cell lysate. All measurements (3 replications of each group) were normalized to the protein concentration of cell lysate, and error bars represent S.E.M., the one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey–Kramer’s post hoc test was used to compare the differences. (C) Fluorescence microscopy images of FITC-labeled peptide P2 (5 µM) incubation with different time point. (D) Fluorescence intensity quantification of FITC-labeled peptide P2 (5 µM) incubation with different time points. Fluorescence intensity was normalized by protein concentration of cell lysate. All measurements (3 replications of each group) were normalized to the protein concentration of cell lysate, and error bars represent S.E.M., the one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey–Kramer’s post hoc test was used to compare the differences. (E) Fluorescence intensity quantification of FITC-labeled peptide P2 (5 µM) with or without trypan blue incubation for 1 h. All measurements (3 replications of each group) were normalized to the protein concentration of cell lysate, and error bars represent S.E.M., the Student t-test was used to compare the differences. (F) Fluorescence intensity quantification of FITC-labeled peptide P2 (5 µM) incubated with or without 5% DMSO treatment for 1 h. All measurements (3 replications of each group) were normalized to the protein concentration of cell lysate, and error bars represent S.E.M., the Student t-test was used to compare the differences.