Fig. 1.
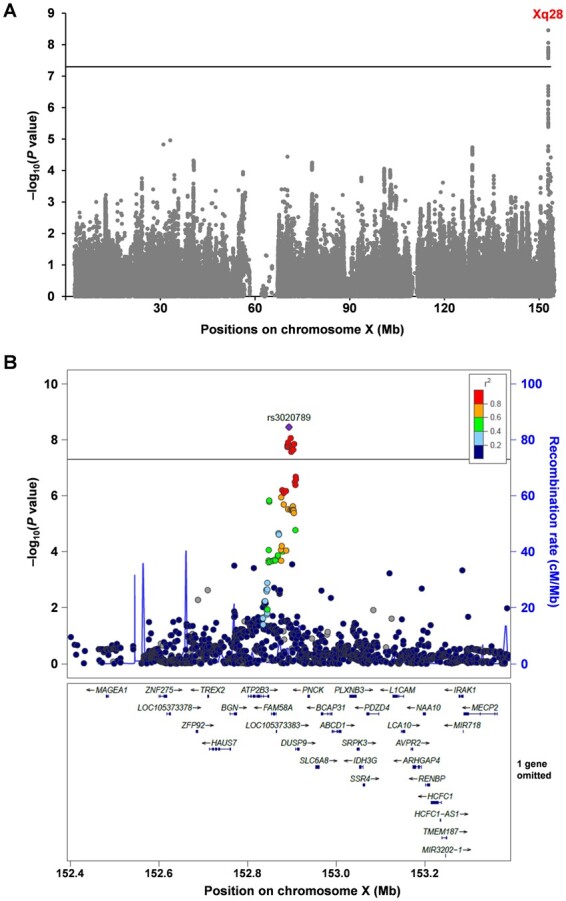
An X chromosome-wide meta-analysis revealed genetic loci influencing serum urate levels in humans
(A) Manhattan plot of the meta-analysis that combines males and females. Supplementary results for males and females alone are shown in supplementary Fig S1A and B, available at Rheumatology online, respectively. (B) Regional association plot for the Xq28 locus identified in the meta-analysis. The vertical axis indicates the –log10(P-value) for the assessment of the association of each SNP with serum urate (SU) levels. The colours indicate the linkage disequilibrium (r2) between each lead SNP and neighbouring SNPs based on female subjects of the JPT population (Japanese in Tokyo) in the 1000 Genomes Project Phase 3 (https://www.internationalgenome.org/home). Horizontal lines represent the genome-wide significance threshold (α = 5 × 10−8). The regional plot was drawn using LocusZoom (http://locuszoom.org/).
