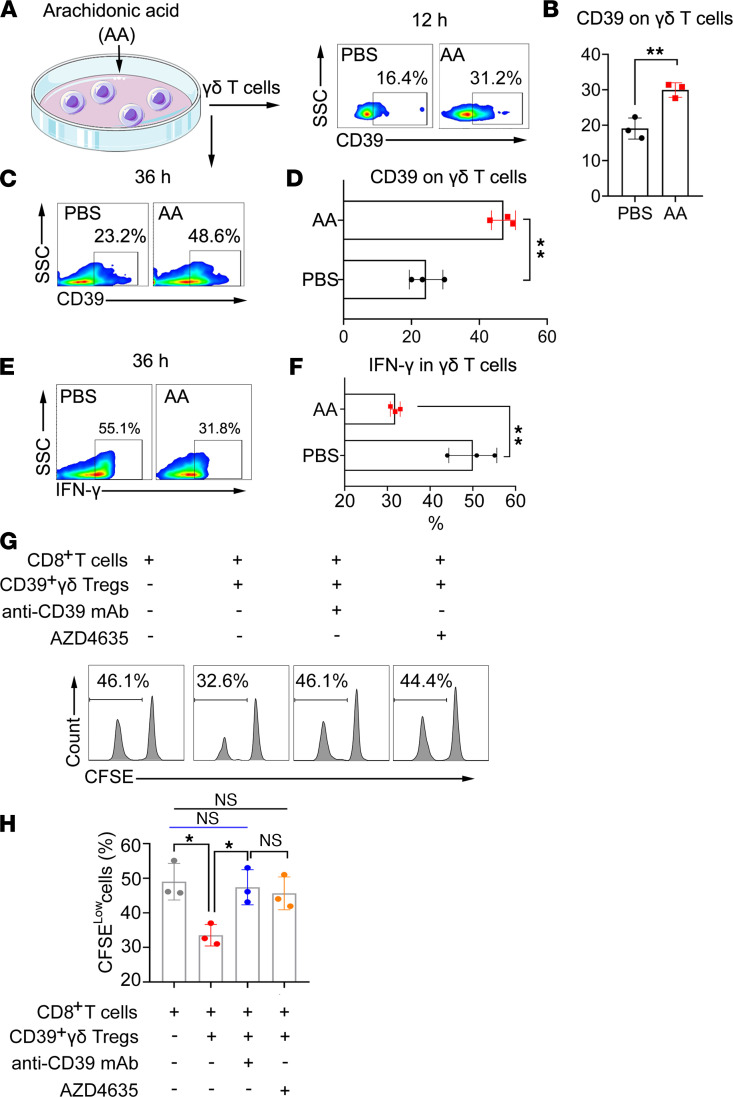
Figure 7. Exogenous AA promotes CD39+γδ Tregs polarization in vitro.
(A–D) Exogenous AA (5 μM) induced the expression of CD39 on γδ T cells. γδ T cells sorted from BALB/c mice were treated with AA (5 μM) in vitro, and the expression of CD39 on γδ T cells was determined by flow cytometry at 12 hours (A) and 36 hours (C). The percentages of CD39 positive cells at 12 hours (B) and 36 hours (D) were calculated and compared using an unpaired t test (n = 3). (E) Exogenous AA (5 μM) decreased the production of IFN-γ in γδ T cells. The percentages of IFN-γ+ cells by intracellular staining at 36 hours (F) were calculated and compared using an unpaired t test (n = 3). (G) AA-induced CD39+γδ Tregs inhibited the proliferation of CD8+cells. AA-induced CD39+γδ Tregs sorted by flow cytometry were then mix with CFSE-labeled αβ T cells from BALB/c mice at a 1:5 ratio and activated by anti-CD3/CD28 mAb with or without anti-CD39 mAb/A2AR inhibitor AZD4635. CFSE was determined by flow cytometry, gating on CD8+cells. (H) Percentage of CFSE-low cells were calculated and compared using 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (n = 3). Data are represented as mean ± SEM of 2–3 independent experiments.