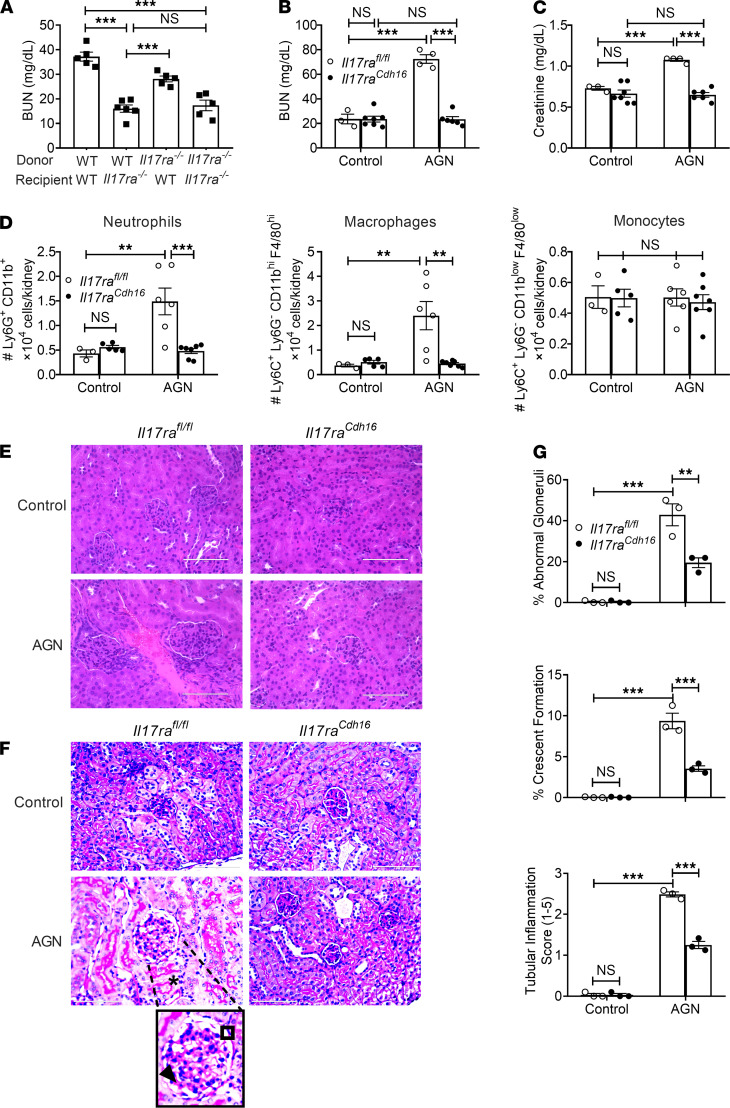
Figure 1. IL-17RA signaling in RTECs is required for AGN.
(A) BM cells from Il17ra−/− (CD45.2+) and WT (CD45.1+) mice were adoptively transferred into sublethally irradiated Il17ra−/− or WT recipients (n = 5–6). Eight weeks later, successfully reconstituted mice were subjected to AGN and assessed for kidney dysfunction by measuring serum BUN levels. Il17rafl/fl and Il17raCdh16 mice (n = 3–7) were subjected to AGN. (B and C) At day 14 after anti-GBM serum injection, serum BUN (B) and serum creatinine (C) levels were measured by ELISA. (D) Neutrophil, macrophage, and monocyte infiltration in the kidney was quantified by flow cytometry at day 7 p.i. (E and F) Representative photographs of H&E-stained (E) and PAS-stained (F) renal histopathology were assessed. (G) Renal pathology was blindly evaluated and scored for percentages of abnormal glomeruli and crescent formation and for tubular inflammation. Data representative of 1 of 3 mice/group for E and F. A small part (as indicated by dotted lines) of the original image (total original magnification, ×400) was shown as inset panels. Open square, indicating entire glomerulus with mesangial and endocapillary hypercellularity; black arrow, GBM thickening; asterisk, tubular atrophy. Data pooled from at least 2 independent experiments. Statistical analysis by 1-way ANOVA (A) and 2-way ANOVA (B–D, G). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.