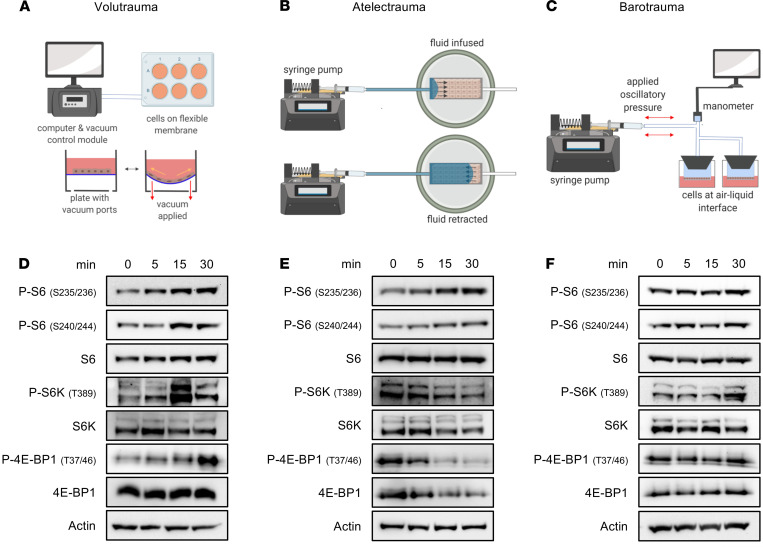
Figure 4. mTORC1 is rapidly activated by volutrauma and atelectrauma in vitro.
Schematics of in vitro volutrauma, atelectrauma, and barotrauma models used (A–D). SAECs were subjected to equibiaxial stretch (20%, 0.2 Hz) for varying amounts of time prior to immunoblotting for markers of mTORC1 activation (protein pooled from n = 3 wells/lane). (E) SAECs were grown to confluent monolayers on collagen-coated glass slides in a microfluidic chamber and subjected to bubble flow (velocity 30 mm/sec) to model atelectrauma for varying amounts of time prior to immunoblotting for markers of mTORC1 activation (protein pooled from n = 2 gels/time point). (F) SAECs were grown at air-liquid interface on Transwells and subjected to oscillatory pressure (30 cm H2O, 0.2 Hz) for varying amounts of time prior to immunoblotting for markers of mTORC1 activation (protein pooled from n = 3 wells/lane).