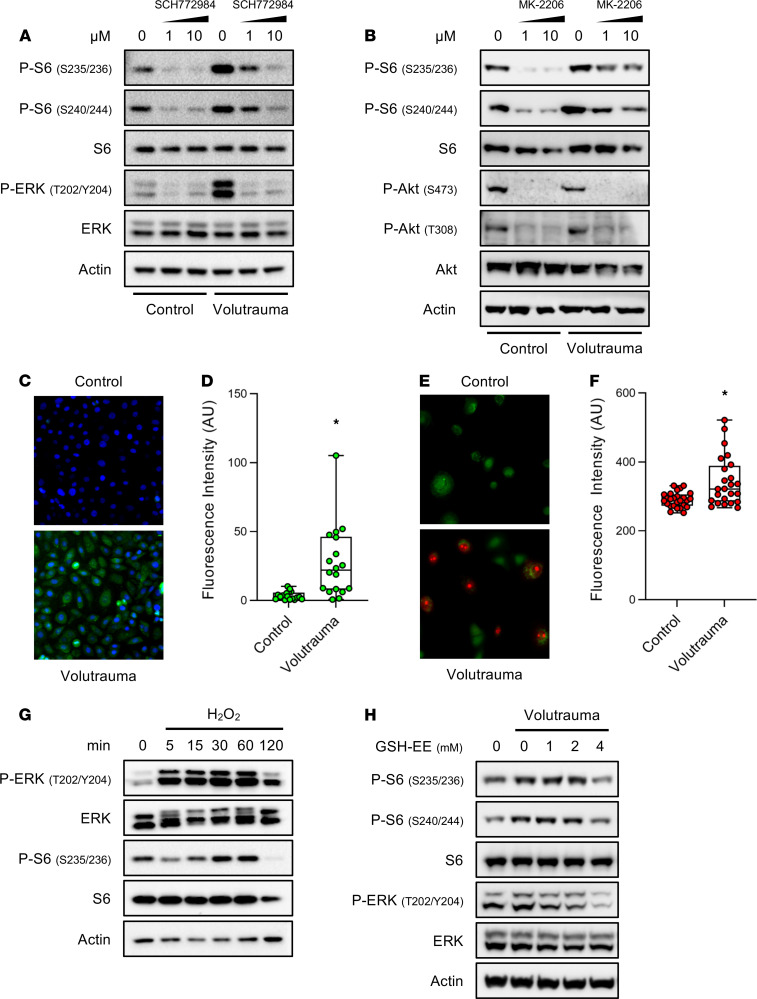
Figure 5. In vitro volutrauma activates mTORC1 through reactive oxygen species-dependent activation of the ERK pathway.
(A) Human bronchial epithelial cells were subjected to volutrauma (20% equibiaxial stretch, 0.2 Hz, 30 min) in the presence of increasing doses of the ERK 1/2 inhibitor (SCH772984) or vehicle (DMSO) prior to immunoblotting for markers of ERK and mTORC1 activation (pooled protein from n = 2 wells/lane). (B) SAECs were subjected to volutrauma (24% biaxial stretch, 0.2 Hz, 30 min) in the presence of increasing doses of the AKT inhibitor (MK-2206) or vehicle (DMSO) prior to immunoblotting for markers of AKT and mTORC1 activation (pooled protein from n = 2 wells/lane). (C and D) HBEs were stretched (24% biaxial stretch, 0.2 Hz, 30 min) in the presence of CellRox Green and fluorescence was quantitated in each field (100×). Data log normally distributed, analyzed by Student’s t test on log2 transformed data (n = 18 fields/group). (E and F) SAECs were stretched (24% biaxial stretch, 0.3 Hz, 30 min) in the presence of mitoSOX (Red) and calcein AM (Green) prior to quantitating the intensity of MitoSOX Red staining in each field (100×). Data not normally distributed, analyzed by Mann-Whitney test (n = 27 images per condition). (G) Small airway epithelial cells were treated with 500 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) for increasing amounts of time prior to immunoblotting for markers or ERK and mTORC1 activation (n = 1 well/lane). (H) SAECs were treated with increasing doses of GSH-EE 30 minutes prior to volutrauma (20% equibiaxial stretch, 0.2 Hz, 30 min) and immunoblotting for markers of mTORC1 and ERK activation (n = 2 wells/lane). Box blots show median ± interquartile range and whiskers define min and max values. *P < 0.05 for all panels.