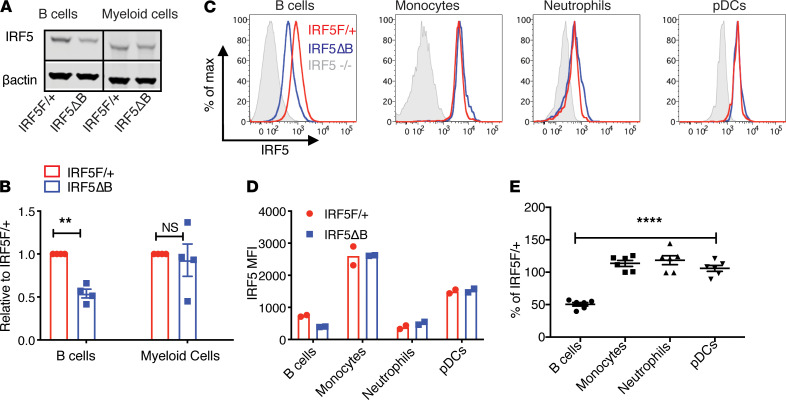
Figure 1. B cell–specific reduction of IRF5 expression in IRF5ΔB mice.
All analyses were done in 8- to 10-week-old FcγRIIB−/−Yaa mice. (A) Representative Western blot of IRF5 protein expression in sorted splenic B cells (CD19+) and myeloid cells (CD11b+Ly6G–) from IRF5F/+ and IRF5ΔB mice. All lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous. (B) Expression of IRF5 in B cells and myeloid cells from IRF5ΔB mice normalized to IRF5F/+ (n = 4). Data were analyzed using 2-tailed, unpaired Welch’s t test; **P < 0.01. (C) Representative flow cytometry plots of intracellular IRF5 expression in CD19+ B cells, CD11b+Ly6C+ monocytes, CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils, and CD11b–PDCA1+Ly6C+ pDCs from IRF5F/+, IRF5ΔB, and IRF5–/– global knockout mice. (D) MFI values of IRF5 in B cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and pDCs from IRF5F/+ and IRF5ΔB mice (representative experiment of 3 individual experiments, n = 2 for each genotype). (E) IRF5 expression in B cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and pDCs from IRF5ΔB mice normalized to the IRF5F/+ littermate control in each experiment (n = 6). Data are shown as mean ± SEM and were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; ****P < 0.0001. IRF5, IFN regulatory factor 5; pDCs, plasmacytoid DCs.