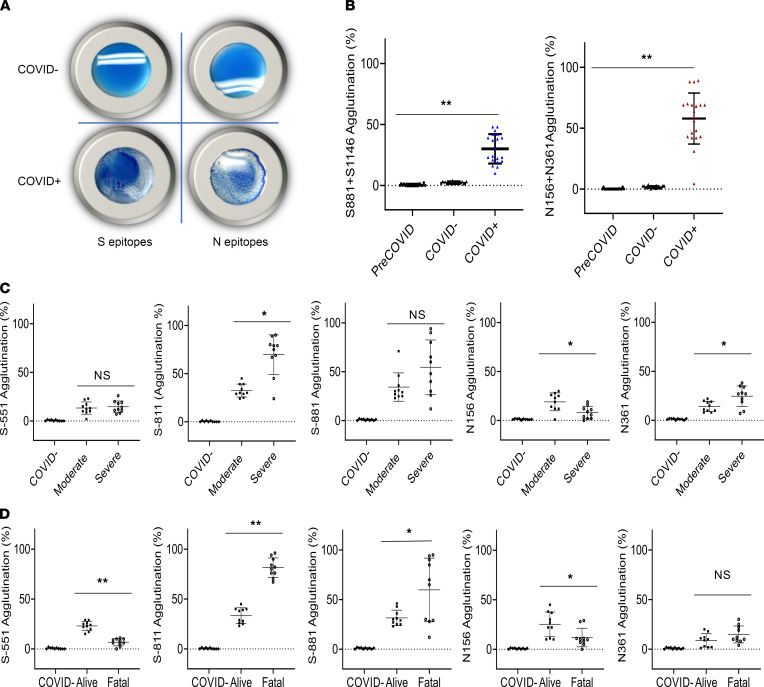
Figure 5. Rapid epitope-dependent agglutination assay for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies effectively differentiates patient groups.
(A) Latex bead agglutination assay to gauge antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2. The latex beads were coated with 1 or more biotinylated S or N epitope peptides and mixed with SARS-CoV-2–negative (COVID–, top) or –positive (COVID+, bottom) plasma. The presence of antibodies against the epitopes promoted the agglutination of the latex beads. Images shown were taken after 2 minutes’ incubation at room temperature. (B) Epitope-based latex agglutination assay distinguished COVID-19+ from COVID-19– or PreCOVID-19 plasma. The epitope peptides used were S-811 and S-1146 from the S and N-156 and N-361 from the N proteins. (C) Correlation of disease severity with antibody responses to the S-811, N-156, and N-361 epitopes determined by latex bead agglutination. (D) Correlation of disease outcome with antibody responses to the S-551, S-811, S-881, and N-156 epitopes determined by latex bead agglutination. P values calculated based on unpaired 1-tailed Student’s t test with Welch’s correction (no assumption of equal SD) (n = 20 for B; n = 10 for C and D). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.002. Error bars represent the SD.