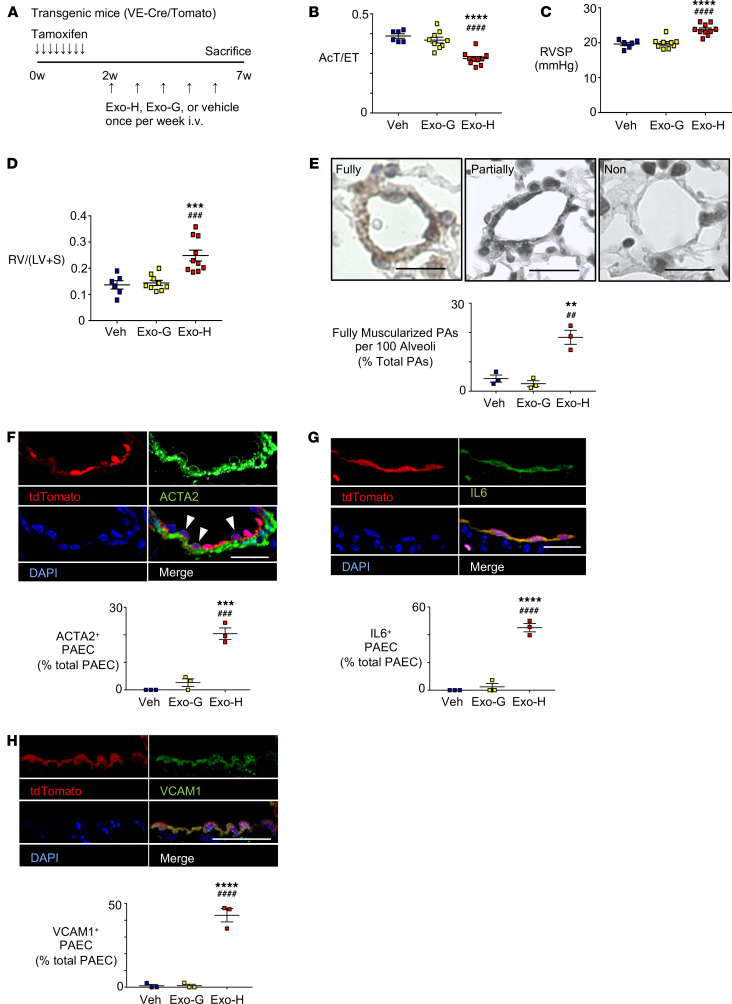
Figure 3. EVs containing HERV-K dUTPase derived from THP-1 monocytes induce PH, EndMT, and a proinflammatory phenotype in mice.
(A) Schema of animal experiments. Adult male mice with an endothelial-specific inducible tdTomato cassette (VE-cadherin-CreER/tdTomato) (VE-Cre/Tomato) received 5 weekly tail-vein injections of EVs (109 particles/g body weight) from culture medium of THP-1 monocytes overexpressing HERV-K dUTPase (Exo-H) (n = 9) or GFP (Exo-G) (n = 9). Control mice were injected with PBS vehicle (Veh) (n = 6). Mice treated with EVs containing HERV-K dUTPase versus GFP exhibited (B) decreased PA AcT per ejection time (AcT/ET), (C) increased RVSP, (D) increased RVH given by the ratio RV/(LV+S), and (E) an increase in the percent of fully muscularized distal arteries from 3 randomly selected mice per group. (F) Immunofluorescence microscopic images show ACTA2 (green) localized to tdTomato (red) positive PAECs (arrowhead) in PAs from endothelial-specific inducible tdTomato mouse. (Images for Exo-G shown in Supplemental Figure 3, E–G). Quantification below shows percent ACTA2 positive ECs of total ECs. Scale bar: 20 μm. (G and H) Images showing tdTomato (red) positive PAECs expressing IL-6 (green) (G) or VCAM1 (green) (H) in PAs from EC fate-mapped transgenic mouse, with quantification of percent IL-6 or VCAM1 positive ECs of total ECs. Scale bars: 20 μm. n = 3 mice in each condition; average of 10 PAs were evaluated per mouse, mean ±SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus Veh and ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 versus Exo-G by 1-way ANOVA and Tukey multiple comparison test.