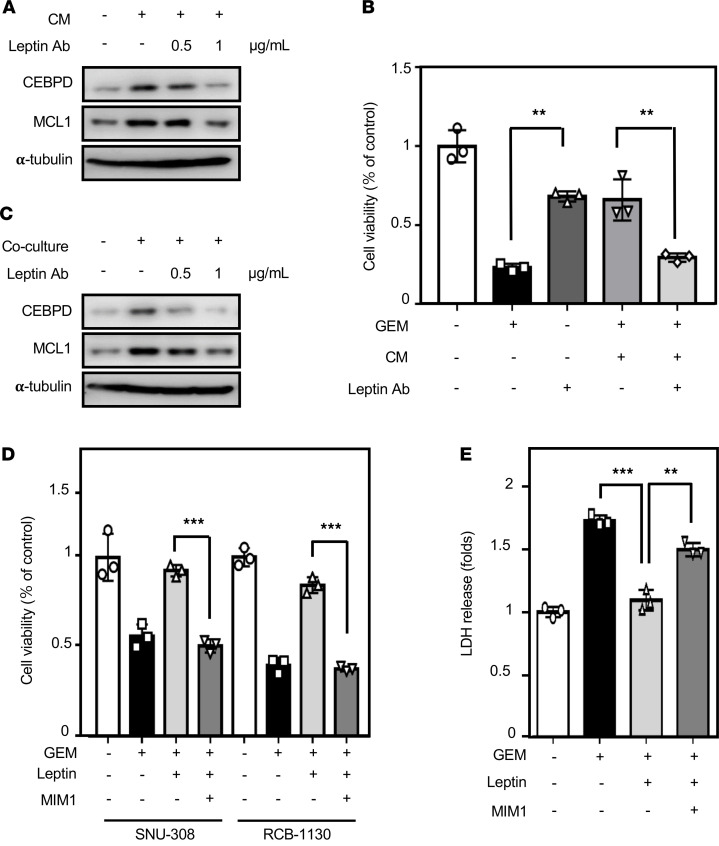
Figure 6. Inhibition of the CEBPD/MCL1 axis enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis.
(A) Attenuation of leptin by neutralized antibody MAB398 inhibits CEBPD and MCL1 expression in RCB-1130 cells. RCB-1130 cells were treated with leptin and with or without MAB398, and lysates were harvested at the indicated concentrations. Antibodies recognizing CEBPD, MCL1, and α-tubulin were used in Western blot analysis (n = 3). (B) Neutralization of leptin resensitizes RCB-1130 cells to GEM. RCB-1130 cells were treated with GEM alone or with GEM in combination with leptin and with or without MAB398. Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay (n = 3; **P < 0.01, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons). (C) Attenuation of leptin inhibits adipocyte-induced CEBPD and MCL1 expression in RCB-1130 cells. Transwell coculture system was used in this study. After 12 hours of coculture with adipocytes, the expression of CEBPD and MCL1 in RCB-1130 cells was examined by Western blot analysis (n = 3). (D and E) The MCL1 inhibitor MIM1 enhances gemcitabine (GEM) sensitivity in leptin-treated GBC cells. SNU-308 and RCB-1130 cells were treated with GEM alone or with GEM in combination with leptin and MIM1 for 24 hours. Cell viability was detected by the MTT assay (n = 3; ***P < 0.001, 2-tailed Student’s t test). Cell toxicity was measured by the LDH assay (n = 3; **P < 0.05, 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons).