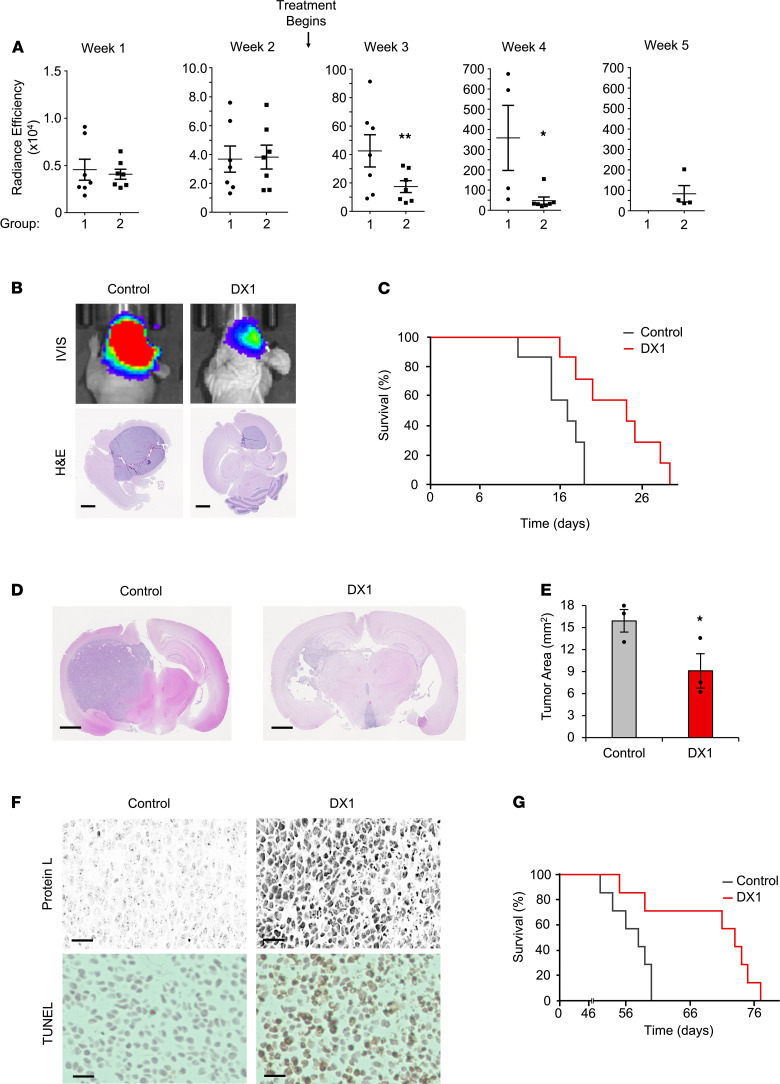
Figure 4. DX1 suppresses tumors in 2 orthotopic PDX models of GBM.
(A–C) DX1 suppresses GBM model 1 tumors. Tumor growth after inoculation of luciferase-expressing GBM model 1 GSCs into the brains of immunodeficient mice was followed by radiance efficiency in the brain by weekly IVIS. Two weeks after inoculation, mice began treatment with i.v. control buffer (group 1) or DX1 (20 mg/kg, group 2). (A) Radiance efficiencies are shown and demonstrate significant suppression of tumors by DX1 (note the y axis scale increases over the weeks). **P < 0.04, Student’s t test, n = 7 per group. *P < 0.02, Student’s t test, n = 4 and 7 per group. (B) Representative IVIS images and H&E stains are shown. Scale bar: 1.25 mm. (C) Treatment with DX1 increased median survival (measured from initiation of treatment) to 24 days, compared with 17 days in control mice (P < 0.01, log-rank test, n = 7). (D–G) DX1 suppresses GBM model 2 tumors. Two weeks after inoculation of GBM model 2 GSCs, mice began treatment with i.v. control buffer (n = 10) or 20 mg/kg DX1 (n = 10) 3 times per week. At 9 weeks after inoculation, brains from 3 mice per group were analyzed by H&E and Ki67 stains to facilitate measurement of mean tumor areas. (D and E) Representative H&E sections and mean tumor areas (*P = 0.04, Student’s t test, n = 3). Scale bar: 1.25 mm. (F) Sections of tumors from mice treated with control or DX1 stained to detect DX1 with protein L are shown and demonstrate that DX1 crossed the BBB to penetrate tumors and was associated with increased TUNEL staining. Scale bar: 50 μm. Results were confirmed by separately staining tumor sections with an anti-DX1 antibody (Supplemental Figure 4). (G) DX1 prolonged median survival in GBM model 2 to 73 days, compared with 58 days in mice treated with control (P = 0.02, log-rank test, n = 7).