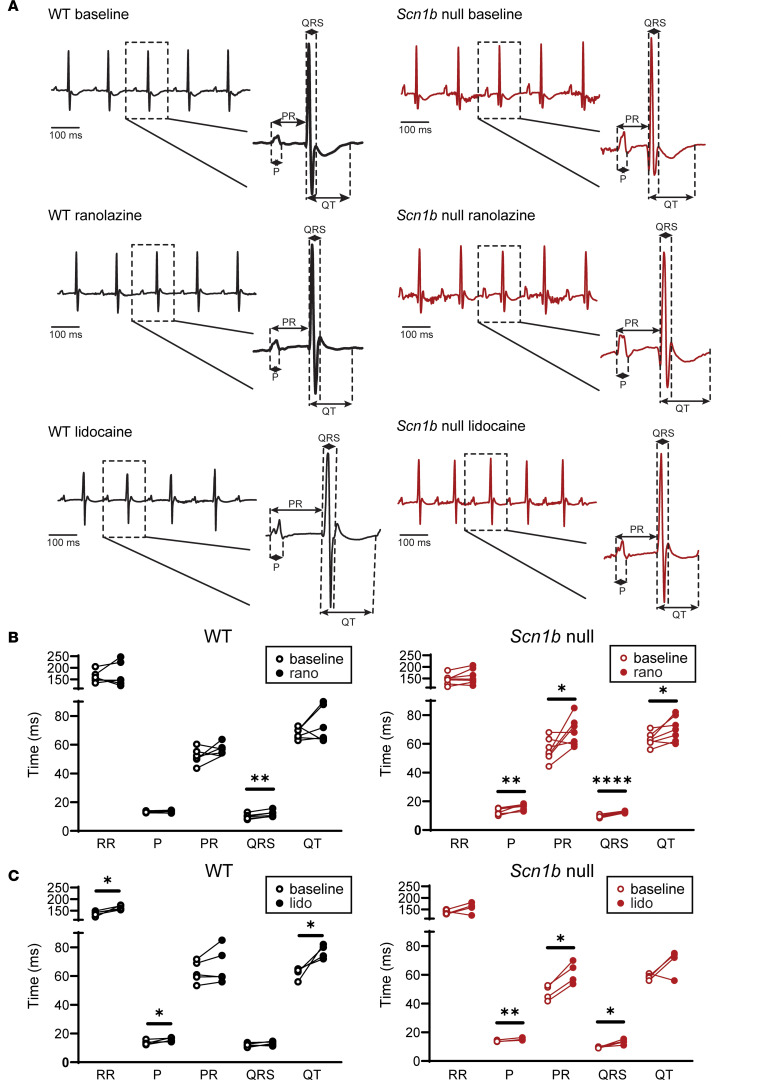
Figure 6. ECG recordings from WT and Scn1b-null mice before and after ranolazine or lidocaine injections.
(A) Representative ECG recordings obtained from WT and Scn1b-null mice at baseline, postranolazine, and postlidocaine are presented. The postranolazine and postlidocaine data were recorded 10 minutes after the i.p. injections of ranolazine or lidocaine. P wave durations, PR, QRS, and QT intervals were measured as indicated in the insets. (B) Comparison of ECG parameters measured in WT (left panel) and Scn1b-null (right panel) mice at baseline and 10 minutes after i.p. injections of ranolazine injection. Ranolazine markedly prolonged the P wave duration and the PR interval in Scn1b-null but not in WT mice. (C) Comparison of ECG parameters measured in WT (left panel) and Scn1b-null (right panel) mice at baseline and 10 minutes after i.p. injections of lidocaine. Lidocaine markedly prolonged the RR interval, P wave duration, and QT interval in WT mice. In Scn1b-null mice, lidocaine also prolonged the P wave duration and resulted in marked prolongation of the PR and QRS intervals. Each data set represents data from 4–7 mice. The ECG parameters and statistical comparisons are shown in Supplemental Table 1.